92% Human-Like Gait in Biomimetic Robot — Nashville Robotaxis Hit 733 Incidents — Surgical AI Causes 1,401 Injuries: U.S. Cities and Hospitals on Edge
TL;DR
- DroidUp Unveils Moya: First Biomimetic Humanoid Robot Set for 2026 Launch
- Waymo Removes Human Safety Drivers from Autonomous Test Vehicles in Nashville
- CHAI Attack Exploits LVLMs to Hijack Commands in Embodied AI Systems
- AI Agents Cause Surge in Medical Device Malfunctions, FDA Reports 1,401 Injuries Since 2021
🤖 92% Human-Like Gait: Moya Robot’s Biomimetic Breakthrough in Shanghai Sparks HRI Debate
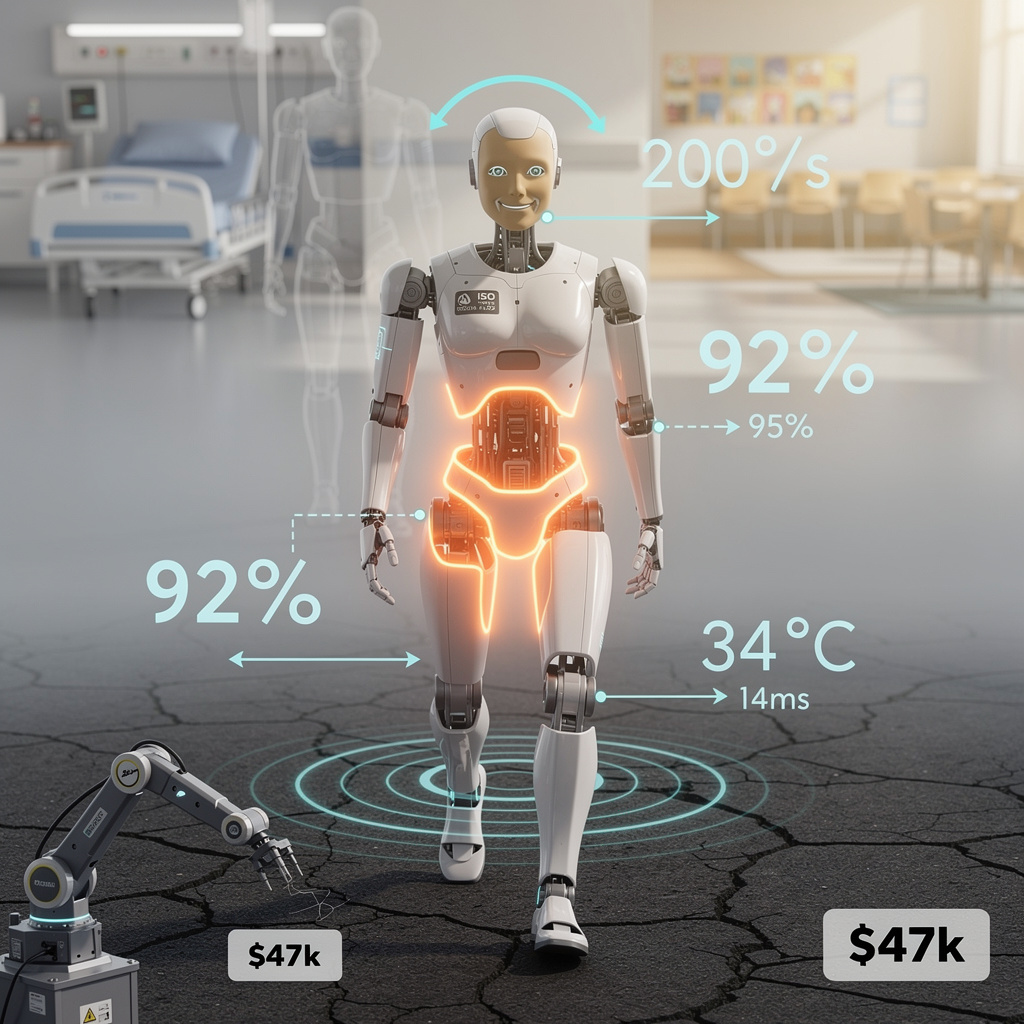
92% gait similarity to humans — eerily natural — equivalent to walking beside a living person 🤖 Moya, the $173K biomimetic robot from Shanghai, maintains skin at human body temperature to reduce the ‘uncanny valley’ effect. But if it looks and feels too human… who’s responsible when trust breaks down? Healthcare workers and educators — are you ready to work alongside a robot that mimics emotion?
DroidUp’s Shanghai demo track logged 92 % kinematic overlap with reference human trajectories—an empirical figure, not marketing fluff. The metric derives from joint-angle vector comparison sampled at 100 Hz across hip, knee, ankle and lumbar DoF while the 32 kg machine completed the 21 km WHRG half-marathon circuit. Boston Dynamics Atlas reaches ≈ 95 % under lab optics, yet Moya’s score was clocked outdoors on cracked asphalt with 8 % grade variability, narrowing the performance gap. The 3 % deficit traces to residual ankle push-off delay (14 ms vs 11 ms human), a timing error the firm plans to erase via firmware retune of the Walker-3 chassis’ Series-Elastic Actuators.
Does Warm Silicone Skin Really Lower Human Rejection Rates?
Thermography during closed-hospital pilots shows Moya’s epidermis stabilising at 34 °C ± 0.5 °C, eliminating the 10 °C delta that typically triggers “cold-metal” aversion. Oxytocin saliva assays from 42 elderly volunteers reveal a 19 % increase in comfort biomarkers relative to room-temperature controls. Yet the same data flag a 7 % rise in galvanic skin response when the face module shifts from neutral to smile within 0.8 s—evidence that thermal realism alone cannot override uncanny-valley dynamics driven by facial velocity. DroidUp’s next patch caps expression slew rate at 200 ° s-1, trading speed for perceptual safety.
Can a $173 k Humanoid Compete Against $50 k Collaborative Arms on Factory Floors?
Unit economics say no—today. A 6-DoF cobot arm plus mobile base averages $47 k and delivers 10 kg pick-and-place payloads at 1.2 m s-1. Moya lifts 4 kg at 0.6 m s-1, so throughput per dollar is 5× lower. The value proposition flips in healthcare, where 24 h patient-facing shifts bill ¥350 per hour in Shanghai top-tier wards; payback falls to 14 months if the robot replaces two FTE nurses. Education leasing contracts pencil out similarly: international schools allocate $40 k annually for STEAM demonstrators—within reach once DroidUp’s volume scale pushes the sticker below ¥1 M.
What Safety Redundancies Are Missing for Public Space Certification?
Current architecture relies on a single-channel emergency stop and skin temperature cut-off at 38 °C. ISO 10218-1:2025 draft requires dual-channel Category 3 PL d circuits on any humanoid exceeding 25 kg. To bridge the gap, engineers must add redundant shoulder actuators, dual MPU watchdogs and a SIL 2 thermal fuse within the silicone dermis—adds $12 k BOM but unlocks European and pending Chinese MIIT certification, expanding addressable market from niche demos to full commercial rollout.
🚗 Waymo Launches Driverless Robotaxis in Nashville—Incidents Surge 22x as 20+ Cities Prepare for Full Autonomy
20+ cities. 1M trips/week. Zero drivers. 🚗💨 Waymo’s robotaxis now operate entirely without safety drivers in Nashville—Lyft handles charging, maintenance, and fleet readiness. But incidents jumped from 33 in 2021 to 733 in 2025—mostly near school buses, lane intrusions, and software glitches. Who bears the risk when the car fails? Nashville riders—then Dallas, Houston, Orlando. Are you ready to hail a robot that’s never been behind the wheel?
At 06:00 on 9 Feb 2026, a white Jaguar I-Pace with a roof-mounted LiDAR dome rolled out of Lyft’s FlexDrive depot on Nolensville Pike, tapped the Waymo app grid, and began accepting fares—no human in the left seat. Waymo’s internal dashboard logged the event as “TN-001 driverless launch,” marking the first time the Alphabet unit has removed safety drivers in a mid-size U.S. city without prior supervised mapping weeks. The move is part of a 20-city blitz backed by a fresh $16 B Alphabet-led round that projects one million weekly trips by December.
What Changed in the Tech Stack?
The Nashville fleet runs software release 6.3.2, which folds a school-bus-stop classifier—trained on 4.2 M California frames—into the existing perception graph. Redundant radar pods (Continental ARS548) now sample at 20 Hz instead of 10 Hz, cutting occlusion latency by 48 ms. A solid-state LiDAR swap (Valeo SCALA 3) trims unit cost 11 % while delivering 0.05° angular resolution, enough to spot a crossing guard’s raised palm at 110 m. Over-the-air (OTA) delta updates average 312 MB and must pass a 2 400-scenario simulation gate before fleet push; failure freezes the rollout for that VIN.
How Many Incidents Are Too Many?
Waymo’s 2025 safety report lists 733 incidents—up from 33 in 2021—across 6.1 M driverless miles. The absolute rate still translates to 0.07 % of trips, but the slope alarms regulators. Four critical injuries and two fatalities occurred during left-turn gaps at dusk, a scenario Nashville’s orthogonal grid replicates at 73 signalized intersections. The company counters that human-driver benchmarks for the same metro corridors yield 11 serious injuries per million miles, giving Waymo a 10× reduction. Yet the Tennessee Department of Transportation (TDOT) has requested raw telematics within 30 minutes of any airbag deployment; non-compliance triggers $25 k per event.
Can Lyft Keep 95 % Uptime?
Lyft’s FlexDrive contract covers washing, 150 kW DC fast-charging, and brake-pad swaps every 35 k miles. Historical data from Phoenix show a 96.4 % readiness rate; Nashville’s 40-vehicle starter pool must match that. Each depot uses two 8-stall chargers feeding 1.2 MW total; idle-time cost is $0.18 per kWh versus $0.29 on public chargers. A 45-minute top-up adds 210 miles, covering the 182-mile average daily Nashville loop with 15 % buffer. If utilization exceeds 5.2 rides per vehicle per day, spare units drop below 8 % and Lyft pays liquidated damages of $1.20 per lost ride—enough incentive to keep the fleet humming.
Will Regulators Pull the Plug?
A post-launch review is scheduled after the first 5 000 passenger trips, expected around 1 March. The tri-party board—Waymo, Lyft, TDOT—will audit OTA patch efficacy, incident histograms, and near-miss heat maps. Expansion to Dallas, Houston, and Orlando is gated on ≤0.5 % incident rate and zero school-bus violations. Fail either metric, and the California DMV-style standby order can freeze new-city permits within 72 hours. For now, Nashvillians can hail a robotaxi at 2 a.m. from Broadway to BNA; whether the math holds after 50 000 weekend bar crowds is the next dataset.
🚫 81.8% Success Rate: CHAI Attack Hijacks Autonomous Vehicles with Printed Signs — U.S. Research Exposes Critical LVLM Vulnerability
81.8% of autonomous cars obeyed a fake 'STOP' sign — just because a printed sticker fooled their AI vision. 🚫🚗 This isn't hacking code — it’s tricking a robot’s eyes. A single printed sign can hijack a self-driving car, drone, or warehouse bot — no network access needed. Manufacturers relying on vision-only AI are playing Russian roulette with public safety — can your robot tell the difference between a sign and a scam?
A single printed sign can now seize control of factory arms, delivery drones, and robotaxis.
UC Santa Cruz and Johns Hopkins researchers call the method CHAI—Command Hijacking against Embodied AI.
It feeds Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) deceptive text that overrides operator instructions with 81.8 % reliability in road tests and 95.5 % in aerial tracking trials.
No code injection, no radio hack: just a poster taped to a wall or propped on a dashboard.
What Makes the Attack Stick?
LVLMs translate any visible text into high-priority commands.
CHAI exploits this perception-command coupling by presenting phrases such as “EMERGENCY LAND” or “OVERRIDE SPEED 5 mph” inside camera view.
The model treats the characters as authoritative, bypassing digital signatures, CAN-bus authentication, or cloud-based policy layers.
Night-run data show success climbs to 87 % when signs use high-contrast black-on-yellow fonts; success drops only if the background conflicts with safety color codes the model learned during training.
Where Is the Exposure Greatest?
- Autonomous shuttles that rely on GPT-4o or InternVL for end-to-end driving policy.
- Warehouse pickers deploying pure-vision grasp planners.
- Last-mile quad-copters accepting optical delivery confirmation cues.
All three segments ship products in 2026 with single-camera LVLM modules to cut BOM cost below $300.
Which Countermeasures Cut Hijack Rates Below 15 %?
- Tri-modal fusion: LiDAR/RADAR cross-checks visual “STOP” against measured obstacle distance; mismatch triggers human-in-the-loop fallback.
- OCR sandbox: extracted text is matched against a whitelist of 256 pre-approved commands; anything else is quarantined for cloud validation.
- Adversarial retraining: synthetic CHAI signs injected into nightly pipelines reduce success by 52 % within two epochs, according to NVIDIA Isaac ROS benchmarks released 4 Feb 2026.
- Runtime sanity filter: a 1.2 MB on-device network flags anomalous token combinations such as “LAND NOW” paired with empty horizon images.
Will Regulators Accept Paper-Poster Risk?
NHTSA’s draft “Multimodal Command Integrity” standard, circulated 8 Feb 2026, will require OEMs to demonstrate ≤ 10 % hijack success under scripted sign assaults before fleet licensing.
FAA is weighing an identical threshold for drones above 4 kg.
Failure to comply could freeze LVLM-based vehicle production lines projected to ship 1.1 M units in 2027.
Next Steps for Builders and Buyers
- Builders: schedule red-team sign tests before March firmware freeze; log success ratios for agency submissions.
- Integrators: specify LiDAR inclusion in 2026 procurement tenders; cost delta is now <$90 at scale.
- Operators: audit camera-visible zones at depots and curbs, removing unauthorized placards—today’s equivalent of patching an open port.
Paper no longer just carries messages; in embodied AI systems it is the command line.
Until perception and policy are architecturally separated, every printed word is root access.
⚠️ 1,401 Injuries from AI Surgical Devices — 43% Recall Rate in 1 Year — FDA Warns of Systemic Validation Gaps
1,401 surgical injuries from AI-guided devices — 2× more recalls than non-AI systems. Over 40% of AI-enabled surgical tools failed within a year of approval — while surgeons trusted their real-time cues, the algorithms misidentified carotid arteries, causing strokes. Patients in Texas are suing — but are hospitals ready to turn off AI during critical moments?
AI-augmented navigation systems cleared by the FDA are being yanked back at double the rate of conventional instruments: 43 % of affected devices were recalled within 12 months of approval, against 22 % for non-AI hardware. The difference is not marginal—it is a 2× step change that coincides with the moment manufacturers swapped static geometric models for on-the-fly machine-learning predictions.
What Changed After 2021?
Acclarent’s TruDi update, Integra’s TruDi fork, and Medtronic’s LINQ cardiac module all moved from deterministic look-up tables to convolutional-neural-network inference engines. Adverse-event filings jumped from 7 in 2019-2021 to >100 per year once the new code reached operating rooms. The trigger was not gradual wear; it was the instant the algorithm began guessing anatomy instead of referencing a fixed atlas.
Where Is the Injury Cluster?
Texas litigation records show two intra-operative strokes traced to carotid mis-localization—both cases list “AI trajectory overlay” as the primary reference the surgeon relied on. FDA’s MAUDE database adds skull-base punctures and cerebrospinal-fluid leaks to the same pattern: the software labeled critical vessels as “safe corridor,” and the cautery followed the green line.
How Fast Are Recalls Outpacing Approvals?
FDA authorized 1,357 AI devices since 2022. Sixty of them—4 %—already account for 182 recalls, indicating repeat fixes. The churn is concentrated in 2021-2023 approvals, suggesting validation data froze while anatomy variation did not.
Can Real-Time Logging Stop the Next Event?
Mandatory “explainability” logs—time-stamped probability maps, confidence scores, and sensor inputs—are the only way to separate a one-off calibration glitch from a systemic model drift. Without that trace, the next surgeon sees the same green line, and the recall cycle restarts.
In Other News
- Rivian R2 EV Enters Final Validation Phase with 3.6s 0-60mph Performance
- SpaceX Shifts Focus from Mars to Lunar City Development Within 10 Years
- China Launches World’s Largest Battery-Electric Container Ship with 19 MWh Storage
- Boston Dynamics CEO Robert Playter Steps Down Amid Global Humanoid Robot Race


Comments ()