AI Startups, OpenAI, Tesla, Airbnb: $500M+ Series D, Data Center Expansion, Pay Package, IPOs Drive Investor Sentiment

TL;DR
- AI Startups Raise $500M+ in Series D Rounds—Metropolis, Synchron, and Others Secure New Capital
- OpenAI Seeks Federal Backstop for Data‑Center Expansion—CFO Sarah Friar Urges Government Guarantees
- Tesla Shareholders Approve Elon Musk's $1 Trillion Pay Package, Voter Concerns Rise
- Airbnb, Groww, Aeroméxico IPOs Drive Investor Sentiment, Shares Rally Amid Revenue Miss
- Seed Rounds Fuel AI Diffusion Models—Inception and Incept Secure $50M Funding
- OpenAI & Microsoft Sign $12B Data Center Build‑Out Agreement, Expanding AI Infrastructure
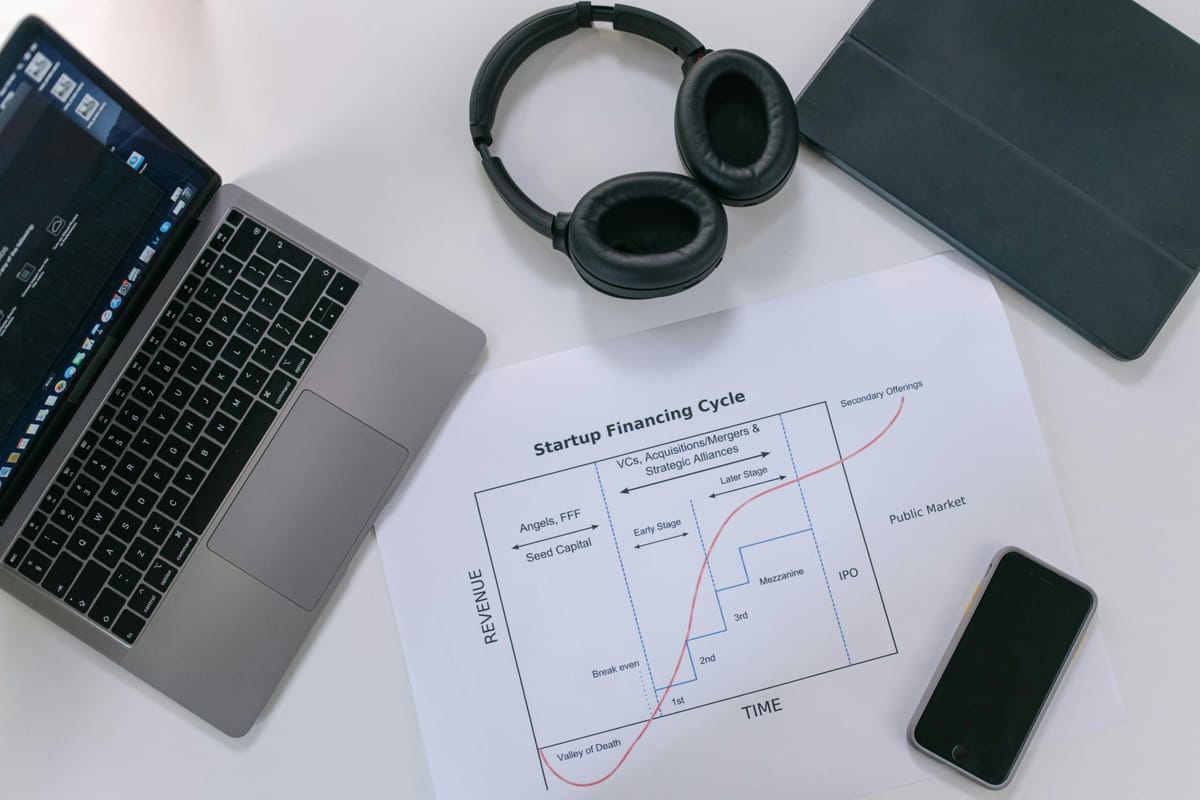
AI Infrastructure Funding Hits New Scale: What the $500 M+ Series D Spree Reveals
Capital Pulse
- Two startups cleared the $500 M Series D threshold on 5‑6 Nov 2025: Metropolis ($500 M equity + $1.6 B debt) and Synchron ($200 M equity).
- Metropolis achieved a $5 B post‑money valuation, representing ~60 % of declared valuations in the window.
- Employee headcount at Metropolis expanded from 2 k to 23 k, directly tied to the capital influx.
- All disclosed deals were US‑based; no non‑US Series D ≥ $500 M appeared.
Financing Mechanics
- Metropolis combined equity with a $1.6 B term loan/credit facility, marking the largest single debt package for an AI startup in this period.
- Lead investors mixed traditional venture (LionTree) with strategic corporate capital (SoftBank Vision Fund 2, BDT, MSD Partners).
- Synchron’s round, though smaller, included an undisclosed syndicate of venture partners, underscoring the role of specialist investors in deep‑tech neuro‑interfaces.
Sector Focus
- High‑value rounds clustered in AI‑infrastructure (Metropolis), neuro‑technology (Synchron), and AI‑driven marketing automation (MoEngage’s $100 M Series F).
- Physical asset intensity—sensor fleets, BCI hardware—drives capital requirements beyond typical SaaS financing.
- Acquisition strategy is evident: Metropolis allocated Series D proceeds to acquire SP Plus ($1.5 B) and Oosto ($125 M) within the same capital event.
Emerging Patterns
- Hybrid equity‑debt structures are gaining traction as AI firms seek low‑interest term loans to fund CAPEX while preserving equity for later rounds.
- The investor mix now includes venture, corporate finance arms, and asset‑management partners, reducing reliance on a single VC class.
- Valuation resilience persists for capital‑intensive AI‑infra firms despite broader market volatility; premium multiples remain for sectors with recurring transaction volumes.
12‑Month Outlook
- Expect 3–4 additional Series D deals ≥ $500 M, primarily in AI‑infrastructure and vertical AI (autonomous logistics, health‑tech).
- Average debt‑to‑equity ratio in these rounds likely to settle near 2.5 : 1, reflecting the Metropolis precedent.
- US will retain > 85 % share of high‑value Series D activity; European pockets may emerge but without comparable debt packages.
- Post‑money caps for AI‑infra startups could rise to $7–8 B if growth rates stay above 40 % YoY.
OpenAI’s Data‑Center Funding: Why a Federal “Backstop” Is Unlikely
From “Backstop” to Clarification
- Nov 5 2025 – CFO Sarah Friar, WSJ Tech Live, suggests the U.S. government could serve as a “backstop” for OpenAI’s data‑center and AI‑chip financing.
- Nov 6 2025 – Friar issues a LinkedIn clarification, emphasizing “government‑enabled financing tools” rather than a direct request.
- Nov 6 2025 – CEO Sam Altman posts on X, denying any formal request for a federal guarantee and pointing to the Chips Act’s loan‑guarantee provisions.
- Nov 6 2025 – Investor David Sacks stresses that no bailout is planned; the focus remains on permitting and grid capacity.
- Nov 7 2025 – White House officials decline to confirm any pending guarantee request, referring to AI as a “strategic asset.”
Financing Gap vs. Existing Policy Tools
- 2025 revenue run‑rate: ≈ $20 B; Q4 2024 loss: $11.5 B.
- Planned infrastructure spend (data‑centers, chips): $1.4 T over ten years.
- Chips Act provisions: $39 B in grants, $75 B in loan guarantees, 25 % tax credit.
- OpenAI’s disclosed “Stargate” deals total $500 B, plus $1 T in contracts with additional chip suppliers.
Near‑Term Outlook
OpenAI is expected to blend private‑equity, corporate debt, and selective use of Chips Act loan guarantees. The strategy avoids a dedicated federal bailout, leveraging established instruments that limit direct taxpayer exposure while reducing capital costs.
Long‑Term Implications
Persistent quarterly losses above $10 B and a $1 T‑plus data‑center commitment could prompt congressional scrutiny. A narrowly scoped guarantee linked to energy‑grid resilience may arise if policymakers treat AI infrastructure as a national‑security priority. Over a three‑to‑five‑year horizon, a permanent “AI Capital Facility” modeled on the semiconductor loan‑guarantee program could institutionalize government‑backed financing, subject to demonstrated public‑interest outcomes.
Tesla Shareholders Approve Musk $1 Trillion Compensation Plan – What It Means for Investors
Shareholder Vote and Immediate Market Reaction
- Approval: >75 % of voting shares at the 6‑7 Nov 2025 Austin annual meeting.
- After‑hours price movement: +2 % on the day of the vote.
- Key dissenters: Norges Bank, CalPERS, Glass Lewis, ISS.
- Key supporters: Robin Denholm (Chair), Dan Ives (Wedbush), several institutional investors such as the Florida State Board of Administration.
Milestones Tied to the Award
- Market‑cap thresholds: $2 tn, $2.5 tn, $3 tn … up to $8.5 tn (12 tranches).
- Operational targets: 20 M cumulative vehicle deliveries, 10 M Full‑Self‑Driving subscriptions, 1 M Optimus humanoid robots, 1 M robotaxi units.
- Profitability metrics: adjusted EBITDA $400 bn and annual net profit ≥ $50 bn.
- Vesting condition: Musk must remain employed for the full 7.5‑year horizon for each tranche.
- Equity award: up to 423 M additional shares (~12 % of total equity), raising Musk’s stake from ~13 % to >25 % if all tranches vest.
Governance and Dilution Concerns
- Potential dilution: 425 M new shares could erode existing shareholder value if milestones are unmet.
- Control concentration: >25 % equity may limit board independence and influence strategic decisions.
- Legal precedent: The 2018 Musk compensation package was invalidated by the Delaware Court of Chancery; ongoing scrutiny could affect this plan.
- Proxy adviser stance: ISS and Glass Lewis advise voting against the award on fiduciary grounds.
Valuation Outlook and Risk Factors
- Projected market cap (linear milestone progression):
- 2026: $2.3 tn (5 M vehicles, 2 M FSD, 0.2 M Optimus, 0.05 M robotaxis).
- 2028: $4.0 tn (12 M vehicles, 5 M FSD, 0.6 M Optimus, 0.3 M robotaxis).
- 2030: $8.5 tn (20 M vehicles, 10 M FSD, 1 M Optimus, 1 M robotaxis).
- Fully vested tranches by 2030 would place Musk’s equity value near $1 trillion.
- Execution risks include supply‑chain constraints for robotaxi and humanoid production, regulatory approvals for autonomous operation, and the ability to sustain high EBITDA growth.
- Even with milestone achievement, the market’s modest post‑vote reaction suggests investors are pricing in significant execution uncertainty.
Investor Sentiment Gains on Airbnb, Groww and Aeroméxico IPOs
Operational Strength Fuels Airbnb Rally
- Q3 revenue $4.10 bn, 30 % below consensus, yet shares rose to session highs on 6 Nov.
- Gross Booking Value up 14 % YoY to $22.9 bn; nights booked up 9 % to 133.6 m.
- Operating cash flow increased 25.8 % to $1.36 bn, offsetting earnings miss.
- Investors focused on demand metrics, viewing the revenue shortfall as a pricing issue rather than a structural weakness.
Robust IPO Demand Across Markets
- Groww (India) achieved 1.88× overall subscription and 5.61× retail subscription; GMP 10 % above the Rs 100 floor price.
- Aeroméxico raised roughly $300 mn; ADR opened at $19.16, a 2 % premium over issue price, with a 5 % discount on private placement indicating strong institutional appetite.
- Both offerings exceeded 1.5× subscription, signalling renewed appetite for equity issuance in fintech and airline sectors.
Sector‑Specific Sentiment Spill‑over
- Travel‑technology (Airbnb) and airline (Aeroméxico) stocks benefited from post‑pandemic travel recovery signals.
- Airbnb’s price advance despite earnings miss coincided with Aeroméxico’s successful debut, creating correlated upside in travel‑related equities.
- Broad market indices showed modest gains (Nasdaq +0.65 %, S&P 500 +0.37 %) while travel and fintech segments outperformed, indicating segment‑driven sentiment.
Near‑Term Outlook (3‑6 months)
- Airbnb: Share price stability with 5‑8 % upside if GBV maintains >10 % YoY growth; margin‑improvement pressure may introduce volatility around earnings releases.
- Groww: Post‑IPO volatility expected in a ±10 % range; long‑run upside linked to user‑base expansion exceeding 30 % YoY.
- Aeroméxico: Potential 8‑12 % price appreciation as Latin‑American leisure travel rebounds and partnership dynamics evolve; exposure to USD‑MXN currency fluctuations noted.
Key Takeaways
- Operational metrics at Airbnb outweighed revenue disappointment, driving a short‑term rally in travel‑tech equities.
- Strong subscription levels for Groww and Aeroméxico illustrate renewed investor confidence in emerging‑market and fintech IPOs.
- Monitoring margin trends at Airbnb, post‑listing liquidity for Groww, and regulatory developments for Aeroméxico will be essential for risk‑adjusted positioning.
AI Diffusion Models Attract $50 M Seed Funding Amid Reliability Concerns
Market Momentum
- Inception secured a $50 M seed round on 6 Nov 2025 to develop diffusion‑based generators for code and text.
- The same week, aggregate AI seed capital reached roughly $5 B across about 20 deals, with similar funding levels ($40‑$80 M) for diffusion startups.
- Funding is concentrated in the United States, with ancillary activity noted in Hong Kong, Europe, and Japan.
Technical Performance
- Demonstrations revealed a 100 % failure rate on a basic password‑change task, highlighting a gap between stochastic generation and deterministic security requirements.
- Sample output included a “Hello World” program in five programming languages, but no evidence of functional correctness beyond syntactic generation.
Emerging Themes
- Venture capital is allocating seed amounts traditionally reserved for later‑stage AI ventures, signaling confidence in the commercial potential of diffusion models beyond image synthesis.
- Analyst commentary stresses the need for robustness guarantees—particularly sub‑1 % failure rates on security‑critical operations—before enterprise adoption.
- Early discourse flags possible labor market impacts, suggesting that regulatory bodies may soon require impact assessments for AI‑generated code.
Timeline
- 5 Nov 2025 – Industry‑wide AI funding surge of $5 B amid market volatility.
- 6 Nov 2025 – Inception announces $50 M seed; demo shows 100 % failure on password update.
- 7 Nov 2025 (forecast) – Potential Series‑A financing contingent on demonstrable reliability improvements.
Outlook
- In the next 6‑12 months, follow‑on Series‑A investments are likely if Inception can achieve >90 % success on deterministic benchmarks such as secure password changes.
- Mid‑term prospects (1‑2 years) favor hybrid architectures that combine diffusion generation with symbolic verification (e.g., theorem proving) and may attract strategic corporate investors.
- Within 12 months, U.S. agencies (NIST, FTC) are expected to release guidelines on AI‑generated code security, potentially mandating audit logs for generated artifacts.
Stakeholder Positions
- Investors and founders argue that diffusion models enable creative software solutions, justifying large seed allocations for first‑mover advantage.
- Analysts and labor representatives caution that current reliability shortfalls and automation risks warrant more measured capital deployment and oversight.
OpenAI‑Microsoft’s $12 B Data‑Center Push Redefines AI Infrastructure
Scale and Spend
- Total eight‑year compute commitment: $1.44 trillion
- Power capacity slated: 30 GW (10 GW Nvidia, 10 GW Broadcom custom, 4.5 GW Oracle, 4.5 GW additional)
- Azure‑centric revenue run‑rate (2025): $20 B, up from $13 B
- Direct Microsoft‑OpenAI facility investment: $12 B
- Ancillary cloud contracts: AWS $38 B (7 yr), Oracle $300 B, UAE‑focused G42 $7.9 B
- Chip inventory commitments: 200 k GB300 (UK/Norway/Portugal/TX), 60 k A100 (UAE)
- Space‑data‑center prototypes: 1 refrigerator‑sized satellite (Starcloud), Google test‑satellite planned for 2027
Diversified Hardware Strategy
OpenAI is moving beyond an exclusive Nvidia reliance. Announced allocations to AMD (10 GW), Broadcom custom ASICs (10 GW), and Intel CPUs create a multi‑vendor ecosystem that spreads risk and drives competitive pricing across the high‑end AI stack.
Multicloud Redundancy
Azure remains the primary training platform, yet parallel contracts with AWS ($38 B) and Oracle ($300 B) provide geographic load‑balancing and protect against single‑vendor lock‑in. This layered approach positions OpenAI to serve enterprise customers worldwide without bottlenecks.
Energy Imperative
Thirty gigawatts of new power demand exceeds the capacity of most regional grids. Statements from both companies reference national grid upgrades toward 100 GW, while exploratory financing for nuclear, high‑efficiency fossil‑gas hybrids, and space‑solar sources signals an emerging “energy‑as‑service” model for AI workloads.
Orbital Prototype Momentum
The launch of the Starcloud satellite and Google’s Project Suncatcher illustrate a nascent shift toward orbital data centers. Continuous solar exposure and freedom from terrestrial land constraints promise higher compute‑per‑watt ratios, potentially delivering a modest share of latency‑sensitive AI services by the end of the decade.
Emerging Trends
- Hybrid compute fabrics combining GPUs, custom ASICs, and CPUs across Azure, AWS, Oracle, and orbital nodes
- Government‑backed loan guarantees reducing capital risk for multi‑trillion AI projects
- Human‑aligned superintelligence research, exemplified by Microsoft’s MAI team, steering product roadmaps toward safety‑centric outcomes
Looking Ahead to 2030
- Annual global AI infrastructure investment projected to exceed $300 B by 2028, with OpenAI‑Microsoft accounting for >15 %
- At least two commercial AI satellites operational by 2029, contributing >5 % of compute capacity for latency‑critical workloads
- AMD and Broadcom accelerators to handle >40 % of OpenAI’s training throughput, reducing Nvidia’s share from ~70 % (2024) to ~45 %
- A U.S. Treasury “AI Infrastructure Credit Facility” of $10 B expected to formalize government financing for data‑center decarbonization
- Microsoft’s MAI‑driven services, such as an Enterprise‑Copilot with built‑in safety constraints, slated for release Q4 2027, aiming to cut external model licensing costs by ~20 %


Comments ()