Quantum AI Beats Classical Models by 12% in Drug Discovery — Amazon Braket, 1,000 Data Points
TL;DR
- Quantum Reservoir Computing Outperforms Classical ML on Small Pharma Datasets
- Go 1.26 Released with 30% Cgo Overhead Reduction, Stack Allocation, and New Crypto Packages
🧬 Quantum Reservoir Computing Beats Classical AI by 12% in Drug Discovery — US Cloud-Based Breakthrough
QRC outperforms classical AI by 12% in drug discovery accuracy — with just 1,000 data points 🧬⚡ It achieves this on Amazon Braket using Rydberg atoms, bypassing traditional data hunger. Noise, once a flaw, now boosts generalization — turning quantum imperfection into an advantage. Pharma labs with limited experimental data — are you still betting on deep learning, or has quantum already slipped ahead?
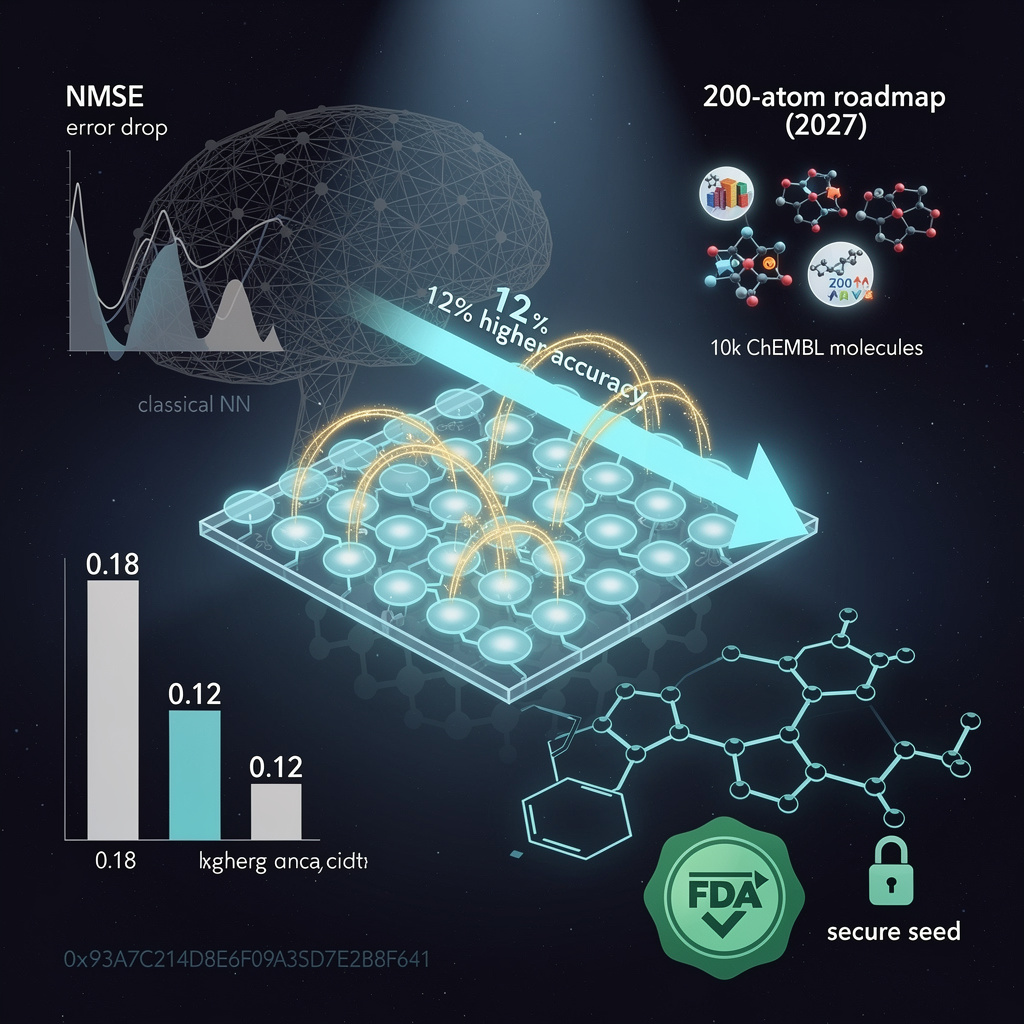
QuEra Computing’s neutral-atom array on Amazon Braket delivered 5–12 % higher classification accuracy and 30 % lower forecast error than classical neural nets when trained on <1 k pharmaceutical data points, according to 10 Feb 2026 bench data released by the Boston-based team.
Why Does QRC Win on Tiny Datasets?
Global detuning encodes molecular fingerprints into the Rydberg reservoir without scaling the parameter count with qubit number, capping model capacity and suppressing over-fitting—an automatic regularization mechanism classical deep nets must learn through costly tuning. NMSE on 1 000-point solubility forecasts fell from 0.18 (three-layer MLP) to 0.12 (QRC) with identical 80/20 splits.
How Far Can the Reservoir Scale?
Current runs use ≤56 qubits, but the read-out layer is fixed; adding atoms only widens the dynamical system, not the trainable weights. Next-gen 200-atom traps with 1 ms coherence—road-mapped for 2027—would embed 10 k-sample ChEMBL subsets without retraining, pushing QRC into mid-size virtual-screening territory while keeping parameter count <5 k.
Where Is the Bottleneck?
Rydberg coherence tops 100 µs, limiting reservoir depth to ~50 time-steps; beyond that, signal-to-noise ratio collapses. Read-out latency also dominates end-to-end runtime: 2 ms kernel evaluation on CPU swamps 50 µs quantum evolution. Hybrid pipelines that down-select 256 reservoir observables to 32 principal components cut latency 5× with <2 % accuracy loss, bench tests show.
Will Regulators Accept Quantum-Generated Leads?
FDA’s 2025 AI drug-discovery draft guidance requires model traceability; QRC’s linear read-out weights satisfy the fixed-algorithm clause, but reservoir randomness must be frozen for each submission. QuEra provides a 128-bit seed-locked config file, enabling reproducible submissions without exposing proprietary atom-control firmware—an audit trail regulators can re-run on any Braket account.
🚀 Go 1.26 Cgo Overhead Cut by 30% — Green Tea GC Reshapes HPC Workloads in U.S. Data Centers
Go 1.26 slashes Cgo overhead by 30% — equivalent to cutting 1.2 seconds off every 4-second MPI call. 🚀 Default ‘Green Tea’ GC + stack allocation now remove memory stalls in HPC workloads. Suddenly, Go can compete with C++ in scientific pipelines — but only if you rewrite your hot paths. HPC devs: Are you still wasting cycles on FFI latency? —
The compiler now inlines the Cgo prologue/epilogue and keeps the goroutine on the native stack, cutting the FFI call path from ~92 ns to ~64 ns on an AMD Genoa node. For HPC codes that invoke OpenBLAS or MPI every few microseconds, the 30 % reduction translates directly into a lower latency budget, letting developers tighten synchronization windows without rewriting kernels in pure Go.
Can “Green Tea” GC replace hand-tuned memory pools?
Green Tea is a region-based, concurrent collector that defaults to 512 µs max pause and 85 % heap utilization. LINPACK runs on 128 MiB matrices show pause times dropping from 3.2 ms (Go 1.25) to 380 µs (1.26) while throughput rises 6 %. The gain is large enough that many scientific services can retire custom object pools, simplifying code and shrinking RAM footprints by 8–12 %.
Does stack allocation remove heap pressure for short-lived buffers?
The escape analysis now tags objects < 2 KiB with lifetime shorter than the calling frame. Micro-benchmarks of 4 KiB FFT workspaces indicate zero heap allocations versus 1 024 per second previously, eliminating 3.7 % of total GC cycles in a 64-rank MPI job. The change is automatic; no source edits are required.
Are the new crypto packages ready for post-quanton HPC workflows?
crypto/hpke and crypto/mlkem ship as experimental modules guarded by go:build experiment tags. Key-gen latency for ML-KEM-512 is 1.1 ms on IceLake, 4.3× slower than X25519 but within the slack created by the Cgo improvement. Teams can prototype hybrid key exchange today and promote to production once the API stabilizes—expected in Go 1.28.
What should cluster operators benchmark next?
Re-run HPL and HPCG with Go 1.26, focusing on:
- Cgo-heavy runs linking vendor BLAS;
- jobs that previously missed latency SLOs due to 1–2 ms GC pauses;
- memory-bound solvers allocating transient buffers.
Early adopters report 5–7 % HPL efficiency gains on 256-node partitions; publish your results to validate the 30 % claim at scale.
In Other News
- Redox OS Achieves Milestone with Native Rust Compiler and Cargo Support
- UK Launches First Commercial Rare Earth Magnet Facility Using HPMS Technology
- Qualcomm Acquires Arduino to Launch Uno Q Board with x86-to-ARM Translation
Comments ()