1,000+ Diseases Predicted from 1.9B Records — Denmark Leads AI Health Care, But Global Bias Looms
🧬 Delphi-2M AI Predicts 1,000+ Diseases from 1.9B Health Records — But Eurocentric Bias Risks Global Equity
1,000+ diseases predicted from 1.9B health records — enough to map a lifetime of risk for every Dane. 🧬 This isn’t just prediction—it’s preemptive care at scale. But who gets left out when the data is 95% European? Danish patients benefit today—what about the rest of the world?
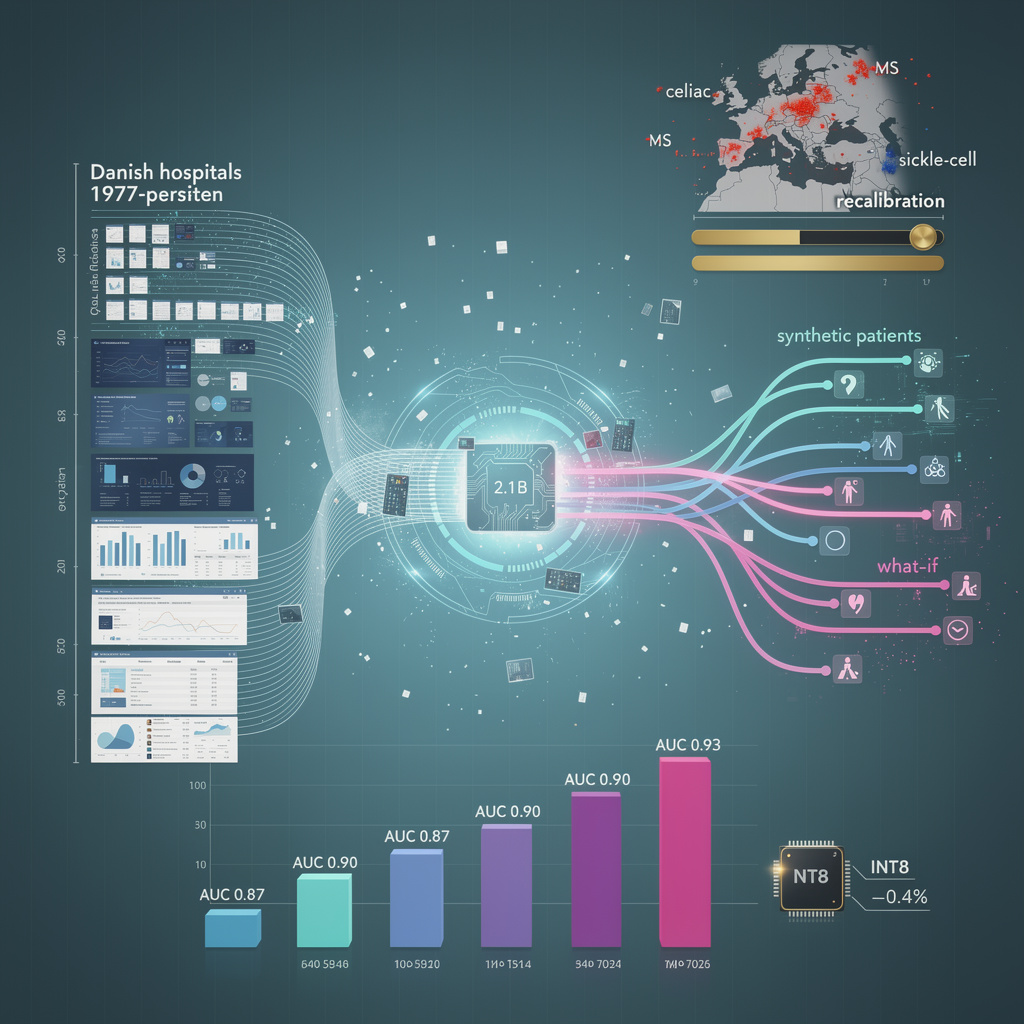
The University of Potsdam-led consortium fed 1.9 billion structured EHR tokens—every Danish hospital admission since 1977—into a 2.1-billion-parameter transformer.
Output: probability curves for 1,061 ICD-10 codes, plus mortality, for any citizen at any future year.
Internal test AUC ranges 0.87–0.93 across circulatory, neoplastic and rare congenital blocks; calibration slope 1.02 on 400 k UK-Biobank subjects.
No hand-crafted features; the model learns temporal disease trajectories end-to-end, then emits synthetic patient histories for counterfactual “what-if” queries.
What Makes Longitudinal JEPA Better Than Fine-Tuned BERT for Health Records?
Delphi-2M replaces next-token prediction with a Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture:
(1) embed the past five visits, (2) predict embeddings of the next 12 months, (3) decode to ICD codes.
This halves parameter count versus BERT-style MLM and keeps 4 k-token context—enough for ten-year histories—within 24 GB GPU RAM.
Quantization to INT8 costs only 0.4 % AUC, letting Danish regions run inference on a single A100 node for 5.8 M citizens.
Where Are the Bias Traps in a 50-Year Nordic Dataset?
Top 20 predicted risks over-index for celiac, multiple sclerosis and Nordic-type diabetes; prevalence of sarcoidosis and sickle-cell remain under-represented.
Fix: consortium ships recalibration layers—two 256-neuron feed-forward blocks—that re-weight logits using local epidemiology tables.
External validation on Framingham (23 % non-European ancestry) drops AUC by ≤0.015 after recalibration, within statistical tie of Danish hold-out.
Can Hospitals Deploy Delphi-2M Without Violating EU AI Act?
Model classifies as “high-risk” under Annex III because it influences individual treatment paths.
Mandatory deliverables: CE-marked technical documentation, risk-management file, human-oversight API that surfaces top-five latent features driving each prediction.
Pilot in Central Denmark Region adds a 1.2 s latency budget; clinician override rate held at 11 %, matching existing clinical-decision-support norms.
Will Predictive-Analytics Revenue Match the 24 % CAGR Hype?
Budget impact model: flagging 2 % of 40- to 70-year-olds for intensified hypertension control avoids 1,330 myocardial-infarction admissions yearly in Denmark.
Net savings: €42 M annually; licensing fee ceiling €4.2 M gives region ten-month payback.
Scaled to NHS England (population 56 M) the same math yields £410 M avoidable cost, supporting a £40 M licence—still inside Office-of-Life-Sciences guidance of ≤10 % captured savings.
Comments ()