AI Reshapes Customer Service Workforce as Small-Cap Stocks Surge and Federal Research Cuts Threaten Ohio’s $149B STEM Economy

TL;DR
- AI-driven automation boosts customer service resolution rates by double digits, reshaping hiring needs for tech support roles
- Federal research funding cuts threaten 41% of U.S. GDP tied to STEM fields, risking Ohio’s $364B economic contribution and 30-35% of its labor force
- Mid-career professionals in Canada’s 55–64 age group contribute 100M+ monthly work hours, facing exhaustion and job loss fears amid caregiving burdens
- AI resume tools improve ATS compatibility and keyword alignment, but recruiters flag robotic phrasing as a growing red flag in job applications
- U.S. small-cap stocks outperform large caps with 15% discount to fair value, signaling investor shift toward mid- and smaller-cap equity opportunities
- Women in Ukraine now register 61% of new sole proprietorships, a 12-point surge since full-scale invasion, signaling gender-driven economic resilience
AI Automation Increases Customer Service Resolution Rates, Redefining Tech Support Hiring Needs
How is AI reshaping customer service workforce structure?
AI-driven generative assistants have increased ticket resolution rates by 10% or more across major contact centers, according to validated pilot data from 2025. These tools provide agents with suggested responses and knowledge-base references, with acceptance rates averaging 85%. Productivity gains are consistent across industries, including finance and telecom, with early adopters reporting 12–15% processing-time reductions.
What hiring changes are occurring in tech support?
Entry-level triage roles are being deferred, with an estimated 0.1–0.2 FTE saved per 10 agents due to efficiency gains. However, total headcount is not declining proportionally. New roles are emerging: Prompt Engineer, AI-Assist Supervisor, Model Auditor, and Trust & Safety Specialist. These positions command average salary premiums of $15,000/year over traditional tier-1 support roles.
How are compliance and data requirements affecting staffing?
Regulatory frameworks such as FedRAMP and Section 508 have extended deployment cycles by 2–3 weeks. Enterprises are adding Compliance Analysts at a ratio of one per 50 agents. Data-fabric investments now consume at least 10% of IT budgets to ensure AI reliability and traceability.
What supervisory structures are being introduced?
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) governance requires one AI-Assist Supervisor per 30 agents to monitor suggestion acceptance rates, audit outcomes, and enforce approval protocols. These roles are critical to maintaining service quality and mitigating AI hallucinations.
How are training and upskilling budgets shifting?
Approximately 15% of total support training spend is being redirected to AI-tool mastery, prompt engineering, and model-audit certification. Organizations are targeting 80% staff proficiency in these areas within six months of deployment.
What is the projected workforce trajectory?
By 2026, net support-tier headcount is expected to decline by 5%, while AI-Assist Supervisor roles increase by 40%. By 2027, prompt-engineer hiring rises 55%, and compliance staffing grows 20%. By 2028, agentic AI may reduce routine-tier headcount by 12%, introducing senior AI-Orchestration leads at a ratio of one per 200 agents.
What is the cost-benefit balance?
AI licensing costs average $90 per agent annually. Productivity gains must exceed this threshold to justify deployment. Enterprises are measuring ROI through tickets resolved per hour, average handling time, and FTE savings—not just query-level efficiency.
Organizations that align hiring with augmentation, compliance, and skill-upgrading—not automation alone—are securing sustainable service quality and workforce resilience.
Federal Research Cuts Risk $150B Ohio Economic Loss and 620K STEM Jobs
How much economic value is at stake if federal research funding is cut?
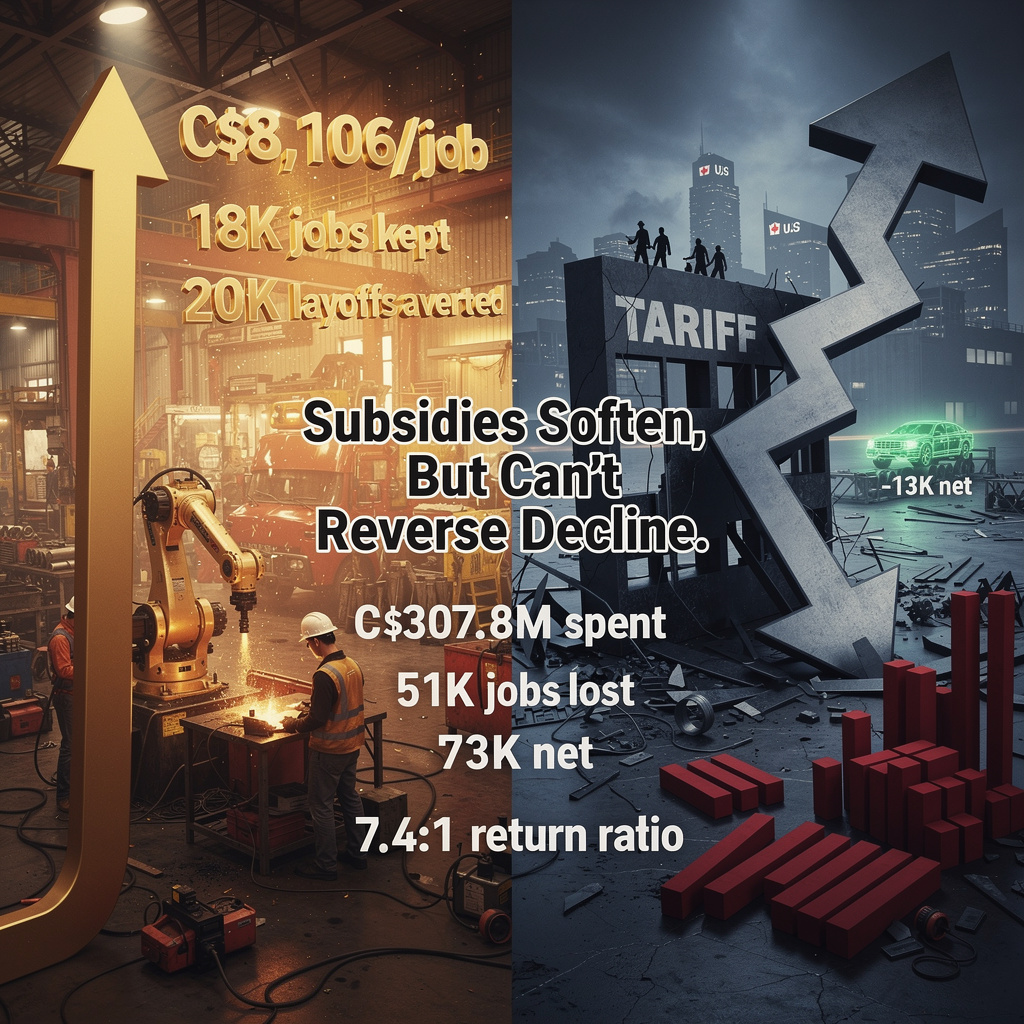
Ohio’s $364 billion contribution to the U.S. STEM economy represents approximately 10% of national STEM-linked GDP. A 41% reduction in federal research funding, as proposed, would directly eliminate $149 billion in state economic output.
What impact would funding cuts have on Ohio’s workforce?
STEM employment accounts for 30–35% of Ohio’s 8.9 million labor force. Proportional cuts to NIH and NSF grants would reduce this segment by 15–20%, resulting in the loss of 420,000 to 620,000 jobs.
How do specific funding reductions affect research capacity?
- NIH budget cut of 37%: Suspension of 1,100 clinical trial grants; 20% decline in public health research capacity.
- NSF budget cut of 50%: Elimination of 1,200 Ph.D. fellowships; 5% reduction in fundamental science contracts.
What is the timeline of federal actions impacting Ohio?
- Jan 15, 2025: NIH grant reviews paused; 1,100 projects halted.
- Feb 3, 2025: NSF graduate fellowships reduced by 50%.
- Mar 10, 2025: Senate restored $5 billion to select health grants—mitigating 15% of projected loss.
- May 22, 2025: Courts reinstated 12 terminated contracts worth $0.8 billion—temporary relief only.
- Dec 30, 2025: Federal freeze on 250 research contracts, including offshore wind and NCAR projects.
- Jan 2026 (projected): Proposed $5 billion STEM Resilience Fund under legislative review.
What are the systemic consequences?
- Each $1 cut in non-defense federal R&D eliminates $1.71 in downstream economic activity.
- Ohio’s research ecosystem is disproportionately exposed due to its concentration of federal grant recipients.
- Judicial reinstatements and partial funding restores do not offset systemic budget erosion.
- Climate science defunding (e.g., NCAR) increases long-term economic vulnerability in flood-prone Ohio regions.
What policy actions could mitigate the impact?
- Legislate minimum 2024–2026 NSF/NIH funding levels to prevent $149 billion GDP loss.
- Establish a STEM Resilience Fund earmarking 5% of federal research budgets for high-impact states like Ohio.
- Preserve Ph.D. fellowships with $250 million allocation to retain talent pipeline.
- Mandate quarterly GDP and labor-force impact reporting tied to federal grants.
- Codify 30-day judicial fast-track for unjustified contract terminations.
What is the projected outcome?
Under baseline conditions (partial restoration), Ohio faces $80–100 billion GDP loss and 200,000–250,000 job losses. Under escalated cuts, losses could reach $130–150 billion and exceed 400,000 jobs. A bipartisan rebound remains unlikely without immediate legislative intervention.
AI Resume Tools Boost ATS Scores but Robotic Phrasing Lowers Interview Rates
Do AI-generated resumes help or hurt job seekers?
AI resume tools increase ATS keyword alignment by up to 23 percentage points, improving pass rates from 65% to 92% when drafts are reformatted into concise bullet points. However, 84% of recruiter-reviewed AI-generated applications contain robotic phrasing—particularly repetitive "responsible for" verbs—leading to a 12-percentage-point drop in interview call rates despite higher ATS scores.
What reduces robotic phrasing in AI resumes?
Human-AI hybrid services, such as ResumeWritingLab.com, cut robotic phrasing detections by 68% while maintaining keyword gains. Bullet-point restructuring, replacing generic verbs with metric-rich language (e.g., "Increased sales by 18%"), appears in 62% of successful resumes versus 19% in rejected ones. Recruiters prioritize quantified achievements as indicators of authenticity and impact.
How do AI screening tools amplify phrasing penalties?
AI-powered interview triage systems, used by 54% of U.S. employers, reduce human interview conversion by 7 percentage points when generic language is detected. This mirrors legal risks seen in the HireVue lawsuit, where opaque AI decisions led to discrimination claims. Automated systems amplify the penalty for unnatural phrasing, creating feedback pressure on resume tools to improve language quality.
What changes are emerging in 2026–2027?
- 2026 Q1–Q2: Major resume platforms will integrate real-time readability scores (e.g., Flesch-Kincaid) alongside keyword metrics, prompting users to revise low-scoring text.
- 2026 H2: Enterprises hiring senior roles ($150k+) will mandate human review of AI-generated drafts, reducing false-positive rejections by 30%.
- 2027: Regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act will require explainable language outputs, forcing vendors to disclose phrase-risk scores and adopt standardized metric-verb libraries.
What actions improve outcomes?
- Resume-tool vendors should auto-convert paragraphs to bullet points and replace weak verbs with curated metric-rich alternatives.
- HR departments should implement human-review checkpoints for high-value roles.
- Career centers should educate candidates on quantified achievement phrasing using proven templates.
AI resume tools are effective for machine parsing but insufficient for human evaluation. The path forward lies in combining algorithmic precision with human linguistic judgment.
U.S. Small-Cap Stocks Trade 15% Below Fair Value as Investors Shift From Mega-Caps
Why are small-cap stocks outperforming large caps?
U.S. small-cap equities delivered a 2.48% return in November 2025, while large-cap indices were flat. This performance divergence follows a sustained 15% discount to fair value, compared to near-par valuation for large caps and a 2% discount for mid-caps.
What is driving the valuation gap?
The discount reflects a re-pricing of risk and growth expectations. U.S. unemployment rose to 4.6% in late 2025, inflation remains elevated at 9.1%, and consumer spending is K-shaped. Small caps, concentrated in energy, industrials, and niche tech, benefit from sector-specific tailwinds and lower valuation multiples.
Is the Fed’s policy stance supportive?
CME FedWatch data shows an 83.9% probability of no rate change in January 2026, with the 10-year Treasury yield at 4.12%. A stable rate environment reduces the cost of capital, enhancing the present value of future earnings for undervalued small-cap firms.
How broad is the opportunity?
Eleven NYSE-listed small-cap stocks trade below $5 per share, signaling expanded investable breadth beyond mega-cap concentration. Sector diversification across energy, automation, and AI-edge technologies reduces idiosyncratic risk.
What does institutional analysis indicate?
Franklin Templeton and LSEG analysts explicitly note a rotation away from mega-caps. Their white paper identifies the 15% discount as a quantifiable arbitrage opportunity, with historical mean-reversion suggesting a 0.4% monthly compression rate under neutral rates.
What is the projected path over the next 12 months?
| Metric | Forecast (Q4 2026) | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Valuation discount | 8% | Historical mean-reversion speed under stable rates |
| Relative outperformance | +1.5% to +2.0% vs. large caps | Momentum and fund-flow continuation |
| ETF inflows (IWM/SMLL) | $3–$5 billion YoY | Institutional reallocation from analyst upgrades |
| Top-performing sectors | Energy (+3–4%), niche tech (+5%) | Energy price stability and AI adoption tailwinds |
What actions are supported by the data?
- Increase small-cap allocation in equity portfolios from 5% to 12% via gradual scaling.
- Build a satellite portfolio of 8 sub-$5 stocks with positive earnings revisions (≥5% YoY).
- Implement a valuation-trigger exit at ≤5% discount to fair value.
- Hedge against reversal risk with a small-cap energy ETF (e.g., XSMC).
- Monitor: discount %, relative returns, ETF flows, and Fed rate probability.
The convergence of valuation, performance, macro, and institutional signals supports a strategic tilt toward U.S. small-cap equities. Discipline in execution and continuous monitoring are critical to capturing the expected 10–12% annualized return over the next 6–12 months.

Comments ()