🦿 $1.5M Humanoid Price Tag: Toyota's Canada Bet Tests Factory Robot Economics

TL;DR
- Toyota deploys seven Agility Robotics Digit humanoid robots in Canadian RAV4 plant, deploying at $1.5M+ cost per unit
- Kollmorgen launches AKME Series servo motors with ATEX/IECEx certification for hazardous industrial environments
- Tesla receives FCC waiver for UWB-based Cybercab wireless charging, advancing fully autonomous fleet with no steering wheel or pedals
🦿 $1.5M Humanoid Price Tag: Toyota's Canada Bet Tests Factory Robot Economics
$1.5M per robot. Toyota just deployed 7 Digit humanoids in Canada—15× the cost of Figure AI's BMW units. 🦿 Bipedal mobility unlocks unstructured factory floors, yet fewer than 20 systems will hit production-grade uptime by 2028. When does $500K/robot become the tipping point for your region's labor market?
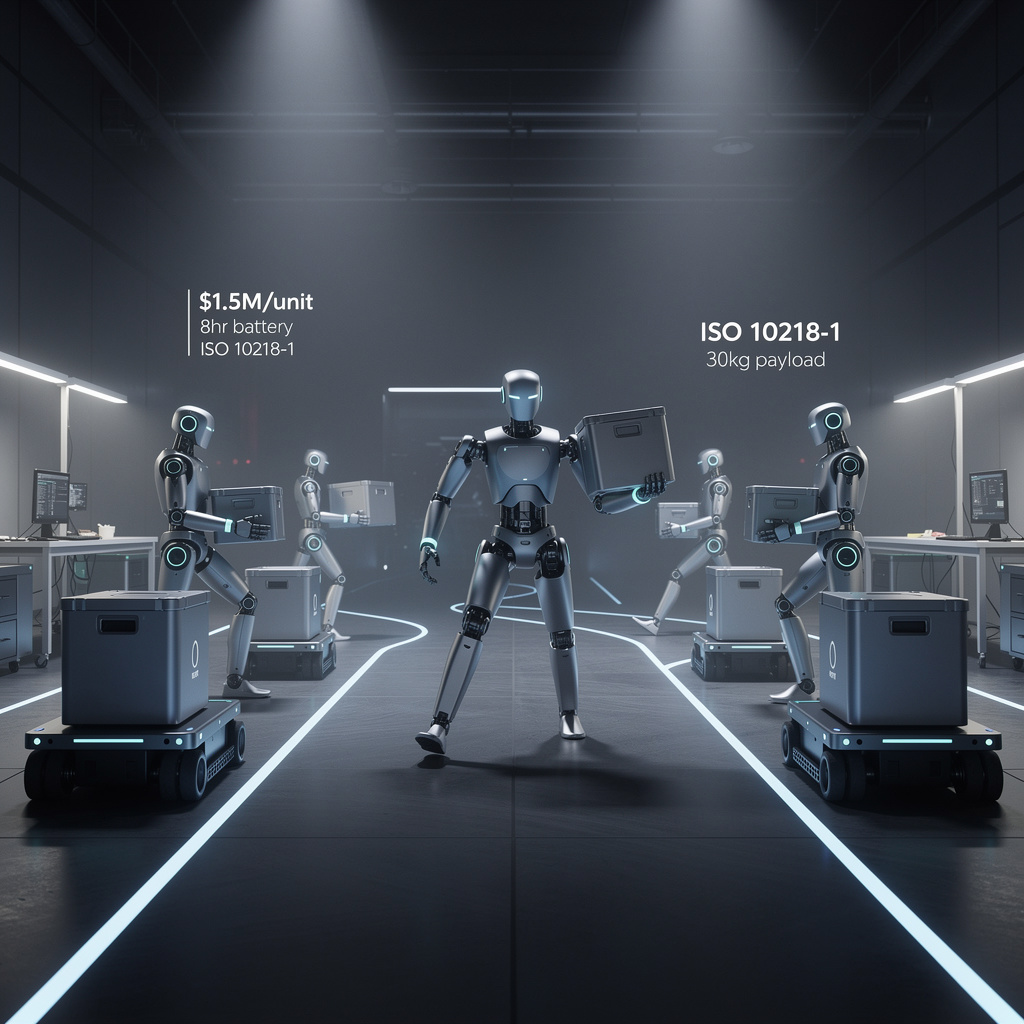
Toyota Motor Manufacturing Canada has placed a high-stakes bet on the future of factory automation. Seven Agility Robotics Digit humanoid robots now unload parts from automated warehouse tuggers at the RAV4 SUV assembly line in Ontario—a deployment costing over $1.5 million per unit. This marks one of the first industrial-scale uses of bipedal robots in automotive production, but the price tag raises urgent questions about economic viability.
How Digit Operates
Each Digit unit navigates unstructured paths between mobile tuggers and fixed workstations, carrying 30 kg payloads on 8-hour battery cycles. The system integrates vision and proprioceptive sensors to generate process data for continuous refinement. Unlike wheeled mobile manipulators—typically offering 12-hour battery life and 15 kg capacity—Digit's bipedal design enables dynamic obstacle avoidance and route reconfiguration without fixed conveyor infrastructure.
Safety compliance demanded extensive customization: TMMC implemented force-limit controllers and redundant emergency-stop networks to meet ISO 10218-1 standards governing collaborative robot operations.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Benefits:
- Labor Flexibility: Eliminates dependence on rigid conveyor layouts, enabling rapid line reconfiguration
- Safety Profile: Bipedal mobility reduces collision risks versus human lift-assist operations
- Data Generation: High-resolution process logging supports predictive maintenance and throughput optimization
Risks:
- Capital Burden: Unit cost exceeds $15–30× conventional collaborative arms (typically $50,000–$100,000)
- Reliability Concerns: Industry forecasts indicate fewer than 20 humanoid systems will achieve production-grade uptime by 2028; current mean-time-between-failures for bipedal platforms remains above 500 hours
- Integration Overhead: Custom safety validation and engineering extended deployment timelines
Competitive Context
The cost disparity with rivals is stark. Figure AI's "Figure 02" robots at BMW—handling 90,000 parts annually at roughly $100,000 per unit—operate at 1/15th Toyota's per-robot investment. Boston Dynamics targets $130,000–$140,000 production costs for Atlas units, with Hyundai projecting 30,000 units annually by 2028. Despite $4.6 billion in 2025 humanoid R&D spending, adoption remains confined to manufacturers with exceptional risk tolerance.
Adoption Trajectory
2026–2027: Toyota will likely expand Digit deployment to two additional lines if throughput, downtime (<2%), and labor cost offset (≥30%) targets are achieved. A 10% unit cost reduction through component bulk pricing is anticipated.
2028–2029: Semi-standardized integration kits—sharing sensor-fusion and motion-planning modules across North American plants—could reduce unit costs to $800,000–$1 million.
2030+: Network-wide deployment of 50+ units may drive total cost of ownership below $500,000, establishing economic viability for facilities with labor rates above CAD $30/hour and flexible-manipulation bottlenecks.
Strategic Implications
Toyota's pilot demonstrates functional feasibility for humanoid manufacturing integration, but the $10.5 million total deployment cost underscores a critical barrier: current humanoid economics favor experimental validation over operational scale. For the broader automotive sector, this deployment signals that bipedal robots remain a strategic hedge against labor shortages rather than a near-term replacement for established automation. Whether the technology matures faster than manufacturing labor costs decline will determine if humanoids become targeted solutions for complex, low-volume production—or costly prototypes that failed to justify their price.
⚡ Kollmorgen AKME: 220 Nm Hazardous-Location Motors Shrink Footprint 12% While Surviving Zone 0 Explosions — Chemical Plants Face Retrofit Decision
220 Nm torque in a housing 12% smaller than legacy servos—built to survive Zone 0 explosions. The AKME Series runs on 4,400 Vac in petrochemical plants where a single spark means catastrophe 🔥 Kollmorgen's integrated flame-arresting barriers just eliminated external gearboxes in confined spaces. But here's the tension: 30% of hazardous motor sales sit in chemical processing, yet most integrators still juggle bolt-on safety devices. Toronto's already live—does your region's certification reciprocity let you skip the red tape?
Kollmorgen has launched the AKME Series servo motors with ATEX/IECEx certification, targeting chemical processing, mining, and oil & gas sectors where explosive atmospheres demand specialized hardware. The February 2026 release introduces IEC frame sizes 2–7, operating at speeds up to 5,000 rpm across a 48 VDC to 4,400 Vac voltage range—an unusually broad span that accommodates both modern low-voltage systems and legacy industrial power distribution.
How does the AKME Series achieve certified performance in confined, explosive environments?
The motors integrate motor, encoder, and sealed stator within a single compact housing, eliminating external gearboxes that expand footprint. Third-party EU laboratory testing validated compliance with ATEX Directive 2014/34/EU and IECEx Standard Ex e-75, covering intrinsic safety, explosion-proof, and dust-ignition criteria for Zone 0, 1, and 2 environments. A 24-bit integrated encoder delivers closed-loop positioning accuracy better than ±5 µm when paired with Kollmorgen's SafeMotion™ Monitor 3.0 firmware, which introduced EnDat 2.2 safe feedback compatibility in January 2026. This combination enables IEC 61508 SIL-2 functional safety without additional external devices.
What measurable impacts does the AKME Series deliver for hazardous-environment automation?
- Footprint efficiency: 12% reduction in overall size versus previous-generation servo solutions, freeing critical floor space in dense plant layouts.
- Torque density: Peak output of 220 Nm (IEC-7 variant at 3,000 rpm), matching or exceeding larger conventional motors.
- Safety integration: Embedded certification and feedback systems reduce engineering overhead for system integrators.
- Voltage flexibility: 4,400 Vac tolerance extends compatibility to petrochemical complexes with legacy power infrastructure.
- Positioning precision: Sub-5 µm accuracy supports high-tolerance applications in chemical processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
What risks remain, and how are they addressed?
Installation integrity represents the primary operational risk. ATEX/IECEx standards mandate certified cable glands, explosion-proof conduit, and proper grounding—failure modes that certification testing addressed through internal flame-arresting barriers, with no ignition incidents recorded under worst-case fault conditions. Periodic gas-group testing and enclosure verification form recommended mitigation protocols.
Where is adoption headed?
- 2026–2027: Initial Toronto and European deployments establish North American and EU reference cases; Toronto validates CSA C22.2 N297 alignment alongside ATEX/IECEx reciprocity.
- 2028–2029: Expansion into greenfield chemical processing projects, where the segment's projected 4.3% CAGR through 2030 drives demand for certified, compact actuators.
- 2030+: Potential standardization across multinational operators seeking unified procurement for global hazardous-location fleets.
The AKME Series demonstrates that hazardous-environment servo motors can compress physical footprint while embedding safety certification at the hardware level—reducing integration complexity for system integrators and accelerating deployment timelines in sectors where explosive atmospheres previously demanded elaborate external protection systems.
⚡ Tesla's 25kW Wireless Charging Cleared: FCC Waiver Enables Steering-Wheel-Free Robotaxi Fleet
FCC just cleared Tesla's Cybercab for UWB wireless charging—25kW, no plug, no driver. That's 56 min for 200 miles while the car parks itself. Meanwhile Tesla robotaxis crash 4× more than humans (1 per 57k mi vs Waymo's 230k). 🚗⚡ So: would you ride a steering-wheel-free taxi in Austin if it meant never waiting for a charger?
Tesla Secures FCC Waiver for UWB Wireless Charging—A Step Toward Fully Autonomous Fleets
The Federal Communications Commission granted Tesla a waiver on February 18, 2026, permitting Ultra-Wideband radio technology for hands-free wireless charging of the Cybercab. This regulatory clearance enables a steering-wheel-free, pedal-free robotaxi to align and charge without human intervention—removing a critical friction point in autonomous fleet operations.
How Does UWB Charging Work?
The system combines Bluetooth Low Energy for initial pad discovery with UWB transceivers operating at 3.1–4.8 GHz to achieve centimeter-precision vehicle positioning. An electronically steered eight-element antenna array on the charging pad then focuses radio frequency energy onto the vehicle's inductive coil. Safety interlocks automatically halt power transfer if misalignment exceeds five centimeters or foreign objects are detected—conditions imposed by the FCC to prevent interference with cellular, Wi-Fi, and dedicated short-range communications systems.
What Are the Operational Trade-offs?
The technical gains carry measurable costs and risks:
- Efficiency: 25 kW wireless transfer refills 65 percent state-of-charge in approximately 56 minutes, versus roughly 30 minutes for conventional plug-in charging—extending dwell time but eliminating connector wear and human handling
- Infrastructure: Pilot deployment begins at 15 high-traffic Supercharger locations in Texas and California during Q2–Q4 2026
- Safety performance: Tesla's robotaxi pilot in Austin recorded 14 crashes across approximately 800,000 miles—about one per 57,000 miles, or roughly four times the human-driver crash rate. Waymo's Level 4 system achieves approximately one crash per 230,000 miles
- Data threshold: Tesla targets 10 billion supervised miles by July 2026 to certify unsupervised operation, having logged 8.2 billion cumulative FSD miles as of February 2026
Where Does This Lead?
2026–2027: Pilot validation of alignment latency under 200 milliseconds and power delivery efficiency above 85 percent across initial pad installations
2027–2028: Expansion to 200-plus pads along U.S. robotaxi corridors, enabling wireless charging for over 90 percent of fleet charging events; integration of UWB positional data into fleet dispatch optimization
2029–2032: Potential reduction in vehicle-hour downtime to under 15 minutes when combined with fast-swap battery buffers; possible industry adoption of connector-less standards enabling vehicle-to-grid services
The FCC waiver establishes a regulatory precedent for RF-based vehicular power transfer. Success depends on closing the safety gap with competitors, scaling pad infrastructure, and securing state-level certifications for wheel-less vehicle designs—steps that will determine whether Tesla's 360,000-unit daily production target translates into operational dominance or stranded capacity.
In Other News
- Toyota shifts RAV4 lineup to hybrid-only powertrains, eliminating gas engines with PHEV model delivering 324 hp and 50-mile electric range
- Lego to launch Smart Brick on March 1, 2026, featuring millimeter-accurate NFC positioning and wireless charging for screenless play

Comments ()