AI Answers Replace 61% of Web Clicks — 12× Conversion Boost at the Cost of Organic Discovery
TL;DR
- AI Search (AEO) Drives 12x Higher Conversion Than Traditional SEO, Forcing B2B SaaS to Rebuild Marketing Strategies
- In-memory SQL engine built entirely by AI outperforms PostgreSQL by 8x in throughput
- AI Agents Now Handle 30% of Airbnb Customer Support Globally
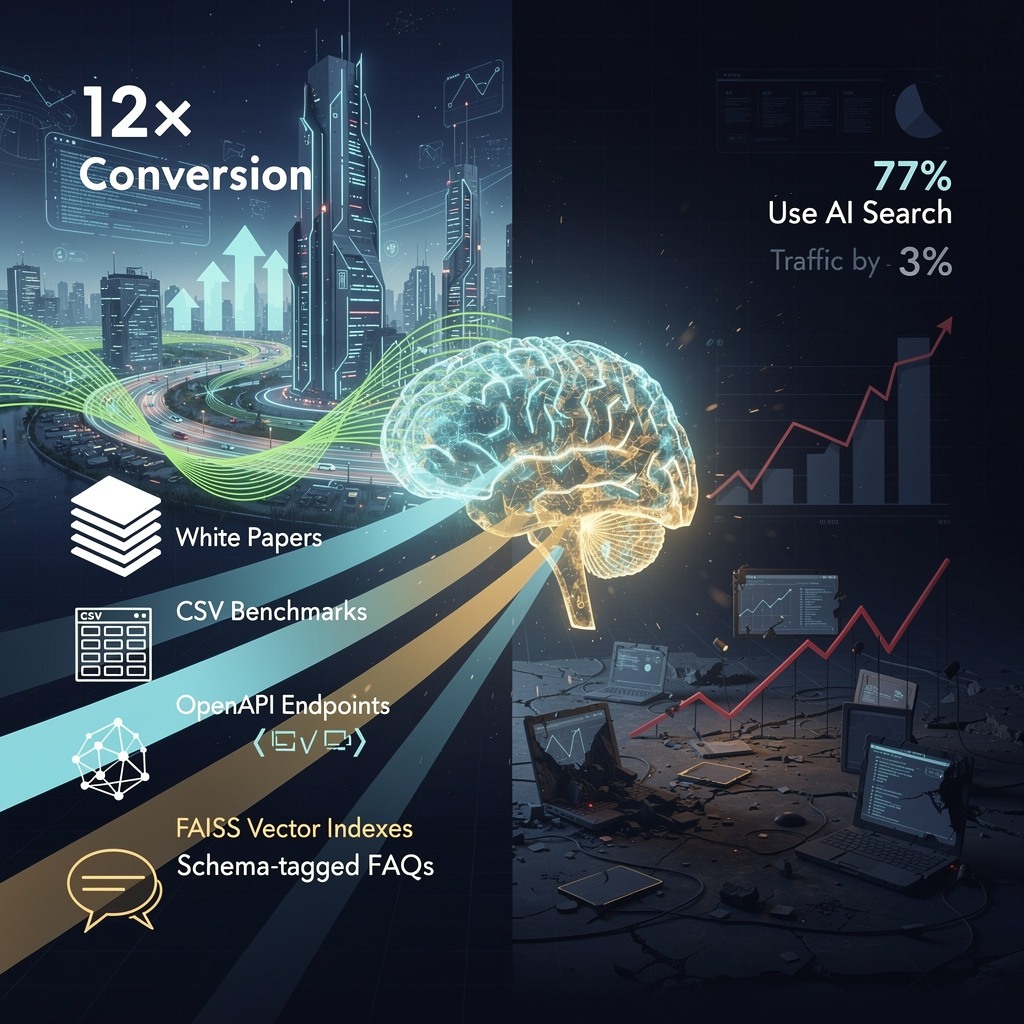
🚀 12× Higher Conversion: AI-Engine Optimization Drives B2B SaaS Growth Amid 61% Organic CTR Collapse in U.S.
AI-driven traffic converts 12× better than organic search — that’s like turning 1 visitor into 12 buyers. But as AI answers replace SERPs, 61% fewer clicks are going to websites. B2B SaaS firms with AI-optimized data are stealing market share from legacy SEO players. Those without structured datasets or API access are losing 40% of traffic. Who’s controlling your discovery channel — Google’s AI, or you?
ChatGPT now doubles as a search engine for 77 % of its 200 million weekly users, and Google’s AI Overviews have sliced organic click-through rates 61 % since last summer. The result: B2B SaaS vendors that secure a citation inside an AI answer convert prospects at 12× the rate of traditional SEO traffic, while brands left out watch their pipelines shrink.
How AEO Works
Instead of chasing keyword rankings, marketers feed large language models directly.
- They publish structured white papers, benchmark CSVs, and schema-tagged FAQs so models ingest authoritative data.
- They expose product specs through OpenAPI endpoints and embed vector-search indexes (FAISS) that assistants can query in milliseconds.
- They court backlink density; Conductor finds a 0.68 correlation between citation count and inclusion in AI-generated answers.
Impacts So Far
- Conversions: 4.4× higher purchase intent for AI-referred sessions; top-cited vendors hit 12×.
- Visibility: 56 % of SaaS sites have zero AI Overview mentions and are down 40 % in organic traffic YoY.
- Competition: Agile newcomers that shipped machine-readable datasets grabbed 12 % of the AI traffic once owned by incumbents.
- Budget shift: CMOs are moving 30–40 % of SEO spend into data-science squads and model-training partnerships.
What Marketers Are Doing—and What’s Missing
- Deployed: schema.org markup, public benchmark files, LLM fine-tuning endpoints.
- Gap: only 1 % of sessions currently come from AI referrals, so attribution models under-report pipeline impact; server-side UTM capture is still rare.
Outlook
- Q3 2026: AI traffic climbs to ~3 % of sessions; organic CTR falls another 10 %.
- 2027: Firms with continuous dataset pipelines project 5–7 % conversion uplift; laggards lose ≥50 % of 2025 search traffic.
- 2029: AEO expected to drive >40 % of B2B acquisitions; traditional SEO becomes a support layer.
Bottom Line
AI Engine Optimization is no experiment—it is already the highest-converting discovery path for B2B SaaS. Companies that institutionalize structured data feeds and API-first content will own the next decade of growth; those that don’t will pay ever-rising ad costs to reclaim an audience that no longer clicks.
🤖 AI-Built MskQL Outperforms PostgreSQL by 9.2× — But Who Maintains It? — Russia
52,670 queries/sec — an AI-built database outperforms PostgreSQL by 9.2× — and it’s just 24k lines of code. No human wrote a single line. The same hardware. Zero external deps. But no replication. No backup tools. No community. — Who loses most when AI replaces decades of open-source engineering? 🤖
A three-agent AI team just did—52,670 insert-queries per second, 8× PostgreSQL’s 5,720 QPS—using nothing but 24 k lines of self-generated C11 and 960+ test cases. Martin S. Kristiansen’s MskQL project shows autonomous code synthesis can beat human-tuned systems on raw throughput while passing every DDL, DML, CTE, and window-function check.
How the engine works
- Lock-free, cache-resident B+-trees eliminate disk I/O.
- Static memory-safety guardrails run in parallel across CPU cores, catching race conditions before they surface.
- Zero external dependencies shrink deployment to a single binary.
Impacts
- Performance: 9× insert throughput, 2× full-scan speed—no new hardware.
- Reliability: 960 automated tests vs. ~300 in typical OSS stacks → earlier defect detection.
- Cost: 24 k LOC vs. 200 k in PostgreSQL core → lower audit and maintenance surface.
- Trust gap: zero human-authored code raises audit and security questions.
Response & gaps
Observed
- Open-source release planned; community replication invited.
- Academic benchmarks published; latency curves included.
Recommended
- Run formal static-analysis (CBMC, Coverity) to complement built-in guards.
- Add replication, backup hooks, and extension API to meet enterprise norms.
- Publish prompt library and model versions for external validation.
Outlook
- 2026: niche adopters fork the repo; expect first external index operator.
- 2027–28: AI-generated variants target time-series & graph workloads; 2–3 commercial proofs-of-concept.
- 2029+: regulatory frameworks emerge for “zero-human-code” certification; bespoke AI engines become orderable like cloud instances.
Kristiansen’s experiment proves AI can out-engineer humans on throughput. The next test is whether it can earn the ecosystem trust that keeps PostgreSQL in production.
🤖 AI Resolves 30% of Global Airbnb Tickets — Human Support at a Crossroads
30% of ALL global Airbnb tickets resolved by AI — no human needed. 🤖 That’s 1 in 3 inquiries handled in 1.8 minutes vs. 4.3 minutes for humans — with higher satisfaction. But what happens when an AI misreads ‘pet-friendly’ and books you into a cat-free apartment? Hosts and travelers in 24 languages — are you comfortable letting AI decide your stay?
How did a 7-billion-parameter model replace one in three human conversations without denting satisfaction?
Airbnb disclosed on 13 February 2026 that its voice-and-chat agents—built on a Meta-Llama-derived, 8-bit quantized, 70% sparse transformer—resolve 30% of all support tickets worldwide. Average handling time has fallen from 4.3 min to 1.8 min, saving an estimated $45 M in annual labor cost while customer-satisfaction scores rose 3.2 points.
How does the system work?
- LLM core: 7 B parameters compressed to 3 GB, auto-scales across Nvidia H100 clusters; latency stays under 150 ms for text, 300 ms for voice.
- Context engine: a 256-d vector updated nightly from bookings, reviews, and host notes lets the bot “remember” preferences across sessions.
- Safety layer: rule triggers (refunds >$500, legal, privacy) auto-escalate to humans; full audit trail satisfies GDPR/CCPA.
Quantified impacts
- Efficiency: 86% first-contact resolution vs. 78% for comparable human chats.
- Scale: 2 M concurrent sessions supported; 24 languages covered.
- Cost: $45 M OPEX reduction equals 12% of global support budget.
- Risk: model drift and hallucination mitigated by nightly retraining and human-in-the-loop thresholds.
Institutional response & gaps
- Observed: Airbnb hired ex-Meta CTO Ahmad Al-Dahle to lead an “AI-native experience” roadmap; competitors such as Airbase reach only 22% deflection.
- Recommended: tighten feedback loops on property-attribute changes and embed federated-learning to curb privacy exposure as contextual data grow.
Outlook
- 2026: pilot AI search for 5% of traffic, pushing deflection toward 35%.
- 2027: dynamic-pricing and host-assist modules target 45% automation and $110 M yearly labor savings.
- 2029-30: federated user embeddings expected to sustain accuracy while meeting emerging data-sovereignty rules.
Airbnb’s production data show that a carefully compressed large-language model can shoulder one-third of global customer care faster, cheaper, and at least as satisfactorily as seasoned human agents. For the hospitality sector, the takeaway is clear: multilingual, context-aware AI is no longer experimental—it is the new baseline for scalable support.
In Other News
- Gemini Chatbot Faces Over 100,000 Distillation Attacks from Commercial Actors
- Nebius Acquires Tavily to Expand Agentic AI Platform
- Heineken to Cut 5,000–6,000 Jobs to Boost Efficiency via AI Automation
- Santa Monica Deploys Hayden AI for Parking Enforcement, Detects 1,100 Bike Lane Violations in 59 Days



Comments ()