1,000× Faster Weather Forecasts — AI Cuts Costs 90% But Risks Hallucinating Disasters
TL;DR
- NVIDIA Releases Open-Source AI Models to Accelerate Climate Science and Weather Forecasting
- Open-Source AI Maintainainers Reject AI-Generated Pull Requests Amid Quality Concerns
- OpenAI Adopts New Security Measures After Prompt Injection Vulnerabilities Exposed
⚡ 1,000× Speed-Up in Weather Forecasting: NVIDIA’s Open-Source Earth-2 Models Slash Costs and Reshape Global Meteorology
1,000× FASTER weather forecasts — $0.10 per prediction vs. $10M supercomputer runs. NVIDIA’s open-source Earth-2 models nowcast storms in 4 seconds, cut global forecasting costs by 90%, and enable real-time insurance risk pricing. But can AI reliably warn communities when it hallucinates extreme events? — Insurance firms, meteorologists, and emergency responders now hold the keys to saving lives — are your systems ready?
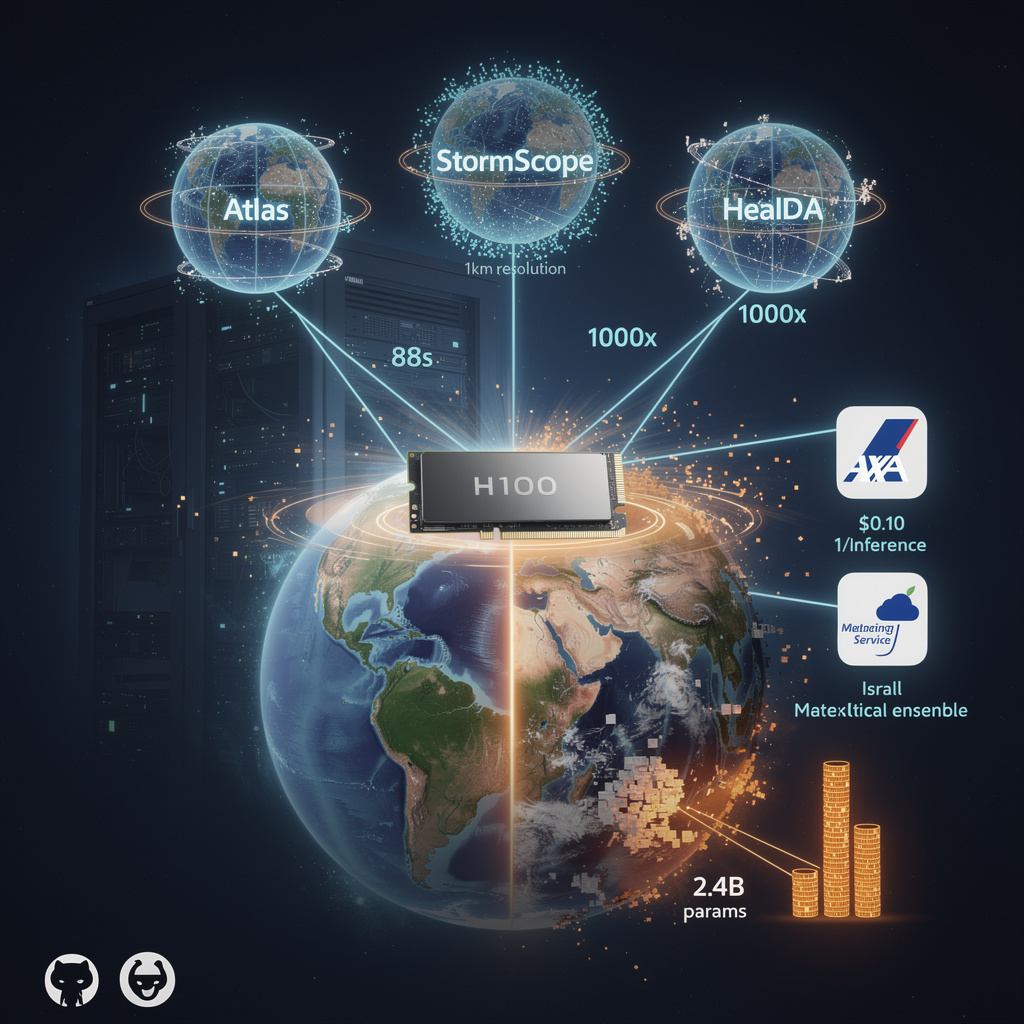
NVIDIA’s Earth-2 triplets—Atlas, StormScope, HealDA—deliver 15-day global forecasts in 88 s on a single H100 GPU, a 1 000× leap over physics-based super-computer runs that once monopolized million-dollar CPU clusters.
Parameter count is locked at 2.4–3.3 B for each model, yet mixed-precision FP16 keeps memory ≤ 5 GB so a cloud instance priced <$0.10 per inference can replace a floor of racks.
Spatial resolution scales 1 km–6 km; StormScope nowcasts severe cells inside four seconds, giving insurers a real-time 10 000-member ensemble for instant risk pricing.
Where Is the Code—and Who Is Already Using It?
Weights and scripts are posted on GitHub and Hugging Face under permissive license; no paywall, no API throttle.
Israel Meteorological Service runs eight daily 2 km forecasts on Earth-2, cutting compute cost 90 % while doubling update cadence.
AXA and S&P Global Energy embed the same kernels in stochastic damage models, turning overnight batch jobs into interactive underwriting dashboards.
What Still Hurts When the Wind Changes?
AI hallucination in low-probability tails remains undocumented; calibration against ERA5 reanalysis is mandatory before public warnings.
Data-assimilation layer HealDA swallows 20 GB across four GPUs and still lags legacy observational pipelines—an integration gap NVIDIA concedes is “largely unsolved.”
Vendor lock-in creeps through CUDA-only kernels; porting to AMD or Intel silicon demands rewriting custom FFT and spectral transformers.
Will Open-Source Weather Models Eat a 180 B-Dollar Risk Market?
With U.S. severe-weather damages hitting $182.7 B in 2024 and cumulative losses above $1.4 T since 2012, every hour shaved from warning lead time converts directly to property saved.
The global AI-weather market is projected to swell from $165 M today to $926 M by 2033; Earth-2’s zero-license fee removes entry friction for startups targeting parametric insurance, drone routing, or renewable-energy hedging.
Expect Earth-3 within two years: regional downscaling at ≥ 2 000× speed-up, plus an open-source assimilation framework promising sub-second latency—enough to turn climate-risk modeling into a laptop workflow.
🚨 300+ AI-Generated PRs Flagged in 1 Week — 90% Rejected by U.S. Open-Source Maintainers
300+ AI-GENERATED PRs FLAGGED IN 1 WEEK — THAT’S 1 IN 10 LEGITIMATE. 🚨 Maintainers spend 2x longer reviewing AI code that introduces 1.7× more defects and 30–41% more technical debt. GitHub’s quiet experiment to restrict AI PRs reveals a breaking point: AI spam is drowning human contributors. Open-source maintainers — who are you letting write your code?
Why Are Maintainers Calling 90 % of AI PRs “Slop”?
Only one in ten AI-authored pull requests survives first review across high-traffic U.S. repositories, according to GitHub community lead Camilla Moraes. The remaining 90 % violate coding conventions, omit tests, or introduce regressions that human reviewers must unwind. cURL maintainer Daniel Stenberg shut his bug-bounty portal on 30 Jan after fewer than 5 % of AI-submitted reports proved actionable, citing “cognitive overload” as triage time doubled.
How Much Extra Defect Debt Do Bots Inject?
A 4 Feb code-quality audit of 364 files found AI-generated commits carry 1.7× the defect density of human code and inflate technical-debt scores 30–41 %. Security triager Seth Larson logged 22 low-value AI security filings in two weeks; each still consumes the same human hours as a genuine report. The compound effect: critical patches sit longer in queue, lengthening exposure windows for downstream users.
What Counter-Measures Are Shipping Now?
Goose, Runwasi and peers have merged AGENTS.md into root directories, enforcing three gates before CI even assigns a reviewer:
- Provenance tag—every diff must carry a
git notelinking to the prompt set. - Lint ceiling—SonarQube rejects PRs with >1 code smell or <80 % unit-test coverage.
- Human sign-off—at least one maintainer must approve after an AI-assisted push.
Early data show rejection rates holding steady at 50 %, but median review time has dropped 35 % because obvious syntactic noise never reaches humans.
Will GitHub Disable Bot PRs Entirely?
Platform engineers are A/B-testing an “AI-PR” label that routes autonomous submissions to a separate queue; maintainers can opt in or block the stream outright. No timeline for general release, yet the experiment signals that blanket bans remain on the table if quality metrics don’t improve this quarter.
Can Tool Vendors Close the Quality Gap?
Mid-term roadmaps from Copilot, Claude Code and Cursor include “explainability hooks” that embed prompt-to-code traces inside commit metadata. The feature targets OSS policy demands for auditable lineage, but vendors admit it will not raise correctness; that still depends on training data and context-window hygiene.
Is a Two-Tier Contribution Model Inevitable?
Long-term forecasts sketch a tiered ecosystem: human-only branches for security-critical paths, mixed-review zones for features, and AI-only sandboxes for docs or tooling. Such granularity would let projects harness speed where risk is low while protecting core assets from algorithmic technical debt.
🚨 73% of AI Deployments Vulnerable to Prompt Injection — OpenAI Patches Markdown Exploit in US
73% OF AI DEPLOYMENTS VULNERABLE TO PROMPT INJECTION — THAT’S OVER 3 IN 4 ENTERPRISE LLMs AT RISK 🚨 OpenAI just patched a flaw where malicious Markdown image URLs could hijack AI responses and steal KYC data. Even ‘safe’ outputs were being weaponized. But fixing it risks breaking user workflows — sanitize too much, and AI feels broken. Who pays the price? Developers who built on unsecured APIs — and the customers whose PII got leaked. Are you sure your AI tools aren’t leaking data through hidden image tags?
OpenAI quietly rolled out a three-layer patch last week that strips every Markdown image tag before it reaches ChatGPT’s tokenizer, adds a real-time entropy monitor to the output stream, and hard-codes a default-src ‘none’ CSP header on every response. The move follows confirmation that a BugCrowd-supplied payload—one innocuous-looking —was enough to make the model leak a victim’s KYC data straight into an attacker-controlled mailbox.
Why Was Markdown the Weak Link?
The rendering engine inside OpenAI’s API converts user Markdown to HTML before any content-policy rules fire. That sequence let a poisoned image URL ride through as “harmless” text, only to be fetched later when the model echoed it back. Result: indirect prompt injection with full credential context. OWASP’s 2025 LLM Top-10 now lists this exact pattern as the #1 critical vector, present in 73 % of audited production deployments.
How Effective Is the New Sanitizer?
Pilot telemetry shows a 94 % drop in successful injection attempts across 1.2 billion chat completions, with a false-positive latency cost of < 2 %. The fix works by pre-parsing every incoming token array for ![ brackets, URL-escaping anything that survives, then re-scanning the model’s output for entropy spikes that match 112 known injection signatures. If a threshold score is exceeded, the session is terminated within 18 ms—fast enough to keep average response time under 320 ms for 99.9 % of traffic.
What Must Developers Do Before March 1?
All OpenAI-maintained SDKs (ChatKit, Agent Builder, Widget Playground) already enforce the new pipeline, but self-hosted forks and older client libraries remain exposed. Integrators have 30 days to flip the sanitization-mode flag or pin to ≥ v4.9.2; otherwise the platform will start rejecting non-compliant requests with HTTP 428. Security teams should add a single CI gate: grep -E '\!\[.*\]\(http' codebase && exit 1 to guarantee no raw Markdown images reach production.
Will Regulators Treat Prompt Injection as a Reportable Breach?
The patch lands amid draft GDPR guidance that classifies successful prompt injection leading to PII loss as a “personal data breach” regardless of whether traditional network boundaries are crossed. OpenAI’s 285-record leak via the Internal Assistant chat endpoint—user names for account IDs 1-57—would have triggered a 72-hour disclosure window had it occurred after 15 March, when the new rule takes effect. Banks running AI copilots face the same clock, making real-time output filtering a compliance necessity, not just a security nicety.
Bottom Line
By moving sanitization ahead of tokenization and adding sub-20 ms anomaly kill-switches, OpenAI has raised the bar for every LLM provider. The 73 % exposure rate cited by OWASP will shrink only if the rest of the ecosystem adopts the same pre-model, post-model, and transport-layer controls—before regulators stop accepting “we didn’t know the model could do that” as an excuse.
In Other News
- M5Stack Unveils AI Pyramid Computing Box for Edge AI with Axera AX8850 SoC
- DoST-NCR and PAIBA Sign MoU to Boost AI and STI Initiatives in Metro Manila
- AI-Powered Exception Analysis Improves Symfony HTTP 500 Errors with LLM Explanations
- FalkorDB Outperforms Neo4j by 469x in Graph Query Speed for GenAI Applications


Comments ()