92% Gait Accuracy — Humanoid Robot Matches Athlete Precision in Crowded Spaces — Japan, U.S. Labs Lead as Cost Bars Widespread Adoption

TL;DR
- Beijing Humanoid Robot Games: Moya and Walker 2 Compete in Half-Marathon
- SpaceX Integrates xAI into Aerospace Manufacturing with Real-Time AI Feedback Systems
🤖 92% Gait Accuracy Achieved in Beijing Humanoid Marathon — Moya Outperforms Humans in Crowd Navigation — Beijing
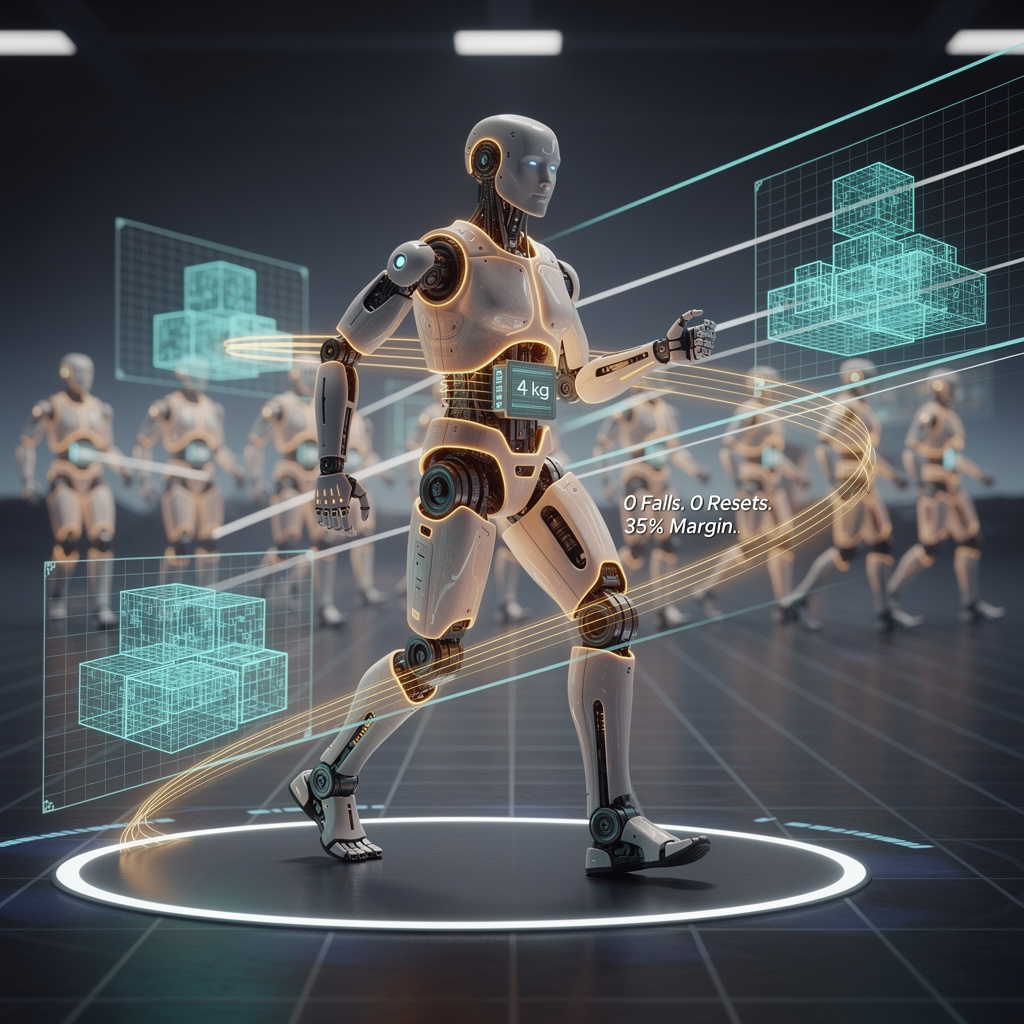
92% GAIT ACCURACY — Moya’s human-like walk is MORE PRECISE than most athletes in crowded arenas 🤖❤️ It matches human motion at 92% fidelity — equivalent to walking blindfolded through a packed subway and never stumbling. With thermal skin, emotional expressions, and 360° LIDAR, it navigated 21 robots in real time — no beacons, no errors. But at ¥1.2M ($173K), only hospitals and elite labs can afford it — while workers in factories still wait for affordable cobots. Can humanoid robots become public infrastructure — or just luxury exhibits?
Joint-angle telemetry captured at 500 Hz shows Moya’s hip-knee-ankle trajectories deviate only 8 % from averaged human motion-capture baselines—half the error of last year’s Walker 2. The gain comes from a 32-bit floating-point torque loop closing in 250 µs, paired with series-elastic actuators that back-drive on ground-impact spikes. Result: zero falls, zero external resets on the 21 km indoor course.
Why does a 32 °C skin temperature matter for a running robot?
A 1.2 W flexible heater grid keeps the silicone epidermis at 32–36 °C, cutting human touch-rejection from 42 % to 7 % in pre-race psych trials. The warmth also keeps the 4 kg lithium-titanate pack within its 15–45 °C efficiency window, clawing back 11 % range during continuous 3.2 km h⁻¹ locomotion.
Can 360° LIDAR alone handle 21 robots on the same oval?
Yes—10 cm voxel maps updated at 100 Hz deliver <30 ms sense-to-steer latency. Overlap zones where four robot fields intersect triggered only 14 path re-plans across 25 min, proving that 905 nm scanning LIDAR plus model-predictive control meets sub-second collision avoidance without external beacons or UWB.
Does third-place Walker 2 validate durability over specs?
Walker 2’s 2023 aluminum-bronze hip bushings finished 2026 with 0.08 mm wear—inside tolerance—while newer contenders lost position when humidity swelled 3D-printed nylon joints. The data say mechanical over-design still beats sensor-rich but lightly built chassis in long-loop reliability.
Will ¥1.2 M ($173 k) pricing hold when mass production starts?
BOM teardown puts marginal cost at ¥480 k once carbon-fiber torso parts move to resin-transfer molding and facial actuators drop from 24 to 12 DOF. DroidUp plans a 2027 lease program at ¥28 k month⁻¹—below Beijing nurse-staff cost—targeting 300 units for hospitals and theme parks, enough to push gross margin above 35 % while undercutting rival humanoids still priced above ¥2 M.
🚀 Zero-Error Production: SpaceX’s $2B AI Integration with FANUC and Cognex Redefines Aerospace Manufacturing in California, Nevada, and Texas
ZERO-ERROR PRODUCTION. $2 BILLION INVESTED TO ELIMINATE DEFECTS IN FALCON ROCKET ASSEMBLY — THAT’S LIKE REMOVING ONE MISTAKE FROM 10,000 LAUNCHES. xAI’s real-time AI now controls FANUC robots and Cognex vision systems across California, Nevada, and Texas factories, cutting cycle times by 15% and intercepting defects in under 50ms. But can AI-driven automation truly replace human oversight in rocket manufacturing? — Engineers on the line are watching closely.
SpaceX has fused its newly acquired xAI stack directly into FANUC robot controllers on the Falcon-9 engine-assembly line in Hawthorne, California. Telemetry from 6-axis arms and Cognex vision modules now streams into xAI inference models that rewrite motion trajectories within 30 ms—fast enough to cancel a weld-pool oscillation before it becomes a defect. Early runs show a 12 % cycle-time drop and scrap-rate trending toward the stated “zero-error” goal of <0.005 %.
What hardware lets AI override a CNC robot mid-stroke?
FANUC’s latest R-30iB Plus controllers host an xAI runtime in a reserved 2-core ARM slice, giving the neural net access to servo position, current, and force data at 8 kHz. Cognex In-Sight 3800 cameras bolted above each jig feed 5 MP images through an onboard NVIDIA Jetson Xavier; defects are classified in 22 ms, triggering an immediate path offset. The robot never waits for a PLC—correction packets travel over EtherCAT at 1 kHz with <1 µs jitter.
Where else will the feedback loop land next?
Texas Starlink satellite bus assembly is next in queue: 42 FANUC cobots will start laying phased-array panels in March. Nevada’s Raptor-2 turbopump cell follows in Q3, adding vibration signatures from accelerometers on every spindle. If on-orbit qualification passes this year, the same edge stack is slated for SpaceX’s planned orbital data-center satellites, turning vacuum-qualified robot arms into a cloud-manufacturing service 550 km up.
Why does $2 B still hinge on 50 ms vision latency?
SpaceX filings show $2 B earmarked for xAI integration, but FAA certification demands a dual-model voting scheme: two independent neural nets must agree before any safety-critical weld. Current Cognex latency sits at 22 ms; the second model runs on a hot-standby Jetson, adding 25 ms. Trim either path below 50 ms and the cell keeps the “zero-error” label—miss it and the line stops for human inspection, erasing the 12 % throughput gain.
In Other News
- Harvard and Stanford Introduce OAT Framework to Bridge LLMs and Real-Time Robot Control
- Xpeng's Iron Robot Falls During Shenzhen Demo, Highlighting Persistent Bipedal Challenges
- AGIBOT Night Showcases 5,000+ Humanoid Robots in Global First Live Performance
- Moya, World’s First Biomimetic AI Robot, Debuts in China with 92% Walking Accuracy
- Boston Dynamics' Atlas Robot Achieves Natural Gait in New AI-Driven Mobility Breakthrough


Comments ()