GM Recalls 80K EVs as BYD’s Mexico Surge Forces Tariffs—Hyundai, Festo, and Roborock Redefine Mobility with AI

TL;DR
- GM Recalls 80,177 Equinox EVs Over Inadequate Pedestrian Warning System
- Hyundai Motor overtakes GM as world’s 4th-most-valuable automaker, deploying Atlas robots in 2028
- Festo Launches AX Motion Insights Platform to Reduce Robotics Downtime via AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance
- Honda CR-V and Toyota Sequoia Lead Longevity Rankings, With 10.6% and 39.1% Probability of Reaching 250,000 Miles
- BYD's $26,307 Dolphin Mini EV Surges in Mexico, Forcing Government to Impose 50% Tariffs Amid 20% Market Share Gain in 2025
- Roborock Saros 20 and Dreame X60 Debut at CES 2026 with Dual Mop Pads, AdaptiLift System, and AI-Powered Cleaning for Hard-Floor Homes
🚨 GM Recall Exposes Critical Flaw in EV Pedestrian Safety Software
GM recalled 80K Equinox EVs because software silenced pedestrian alarms below 30 km/h. 27% false-negative rate. $180M repair cost. $401M penalty risk. OTA fixes help—but hardware delays threaten compliance. Safety isn't a firmware toggle.
GM recalled 80,177 2023–24 Chevrolet Equinox EVs due to a firmware flaw that disabled the Acoustic Alert Unit (AAU) at speeds ≤30 km/h, violating FMVSS 138. The defect caused a 27% false-negative rate in pedestrian warning sounds—hardware was intact, but software suppressed output.
Remediation is tiered: 70% of vehicles receive an OTA firmware patch; 22% require a dealer-installed speaker-array retrofit (parts from Puebla, Mexico); 8% need full AAU replacement. Direct repair costs total $180.4M, with an additional $2,250 average per-vehicle expense (parts $1,500, labor $600, logistics $150).
NHTSA’s non-compliance notice (2025-01-37) exposes GM to a potential $400.9M civil penalty—calculated at $5,000 per unit. Brand-revenue drag is estimated at $1.9B, driven by consumer trust erosion in GM’s EV safety protocols.
GM’s existing OTA infrastructure, validated by a January 13, 2026, Electronic Power Management update, enables rapid software fixes. However, hardware retrofits face a 4-week supply delay from Puebla, risking compliance bottlenecks in high-density markets like California and New York.
NHTSA’s 90-day compliance deadline requires >95% repair rate. If below 90%, penalty enforcement is likely. A post-recall audit may uncover 12,000 additional 2024 models with the same firmware, adding $27M to costs.
Mitigation priorities: expedite speaker-module logistics, deploy multi-channel recall alerts with loaner vehicles, establish a joint GM-NHTSA compliance task force, and embed automated FMVSS 138 testing into Ultium QA by Q3 2026.
This recall is not a software glitch—it’s a systemic QA failure in safety-critical autonomous vehicle subsystems. GM must now prove its EV platform can reliably meet regulatory thresholds—not just performance targets.
🤖 Hyundai Overtakes GM as Top 4 Automaker via Atlas Robot Deployment
Hyundai just surpassed GM in market cap ($61B) not just from EV sales—but by deploying 5,000 Atlas robots in 2028 to cut EV labor costs by 5%. 7% faster assembly. 12% fewer reworks.
Hyundai Motor Group surpassed General Motors as the world’s fourth-most-valuable automaker in January 2026, with a market cap of $61 billion (≈98.3 trillion KRW), driven by a 16% KOSPI surge on January 19. Jan–Nov 2025 sales reached 566k units—just above GM’s 560k—fueled by an 8% revenue lift from EVs (IONIQ 5, Tucson EV) and the Grand i10’s 19.6% volume growth.
Can Humanoid Robots Cut EV Production Costs by 5%?
Hyundai will deploy 5,000 Boston Dynamics Atlas humanoid robots at its Savannah, GA plant in 2028, scaling to 20,000 by 2030. Each Atlas unit has 56 degrees of freedom and handles 50kg payloads—enabling precise battery-pack insertion and torque-controlled fastening in temperature ranges from –20°C to +40°C, certified to ISO 10218-1.
Pilot data shows a 7% cycle-time reduction (35s → 32.5s) and 12% fewer reworks. Projected labor savings: $12 per $240 EV unit. Full rollout targets a 5% labor-cost reduction per vehicle by 2030.
Is Hyundai’s Robotics Strategy Unique?
Yes. Among global automakers, Hyundai is the only Tier-1 OEM deploying humanoid robots at scale. Competitors like GM, Ford, and VW remain reliant on fixed-axis robotic arms. Atlas units enable dynamic handling of semiconductors, actuators, and EV modules, reducing single-source supply chain risks.
What’s the Timeline for Full Deployment?
- 2028: 5,000 Atlas units deployed on battery-pack sub-assembly lines; target: 5% labor-cost reduction.
- 2029: +5,000 units on power-train lines; target: 8% OEE uplift.
- 2030: +10,000 units on interior-trim lines; target: 12% re-work reduction fleet-wide.
What Risks Could Delay This?
- Actuator supply bottlenecks (mitigated by Q2 2027 long-term contracts).
- AI-software integration with autonomous vehicle control stacks (mitigated by joint R&D fund with Boston Dynamics by Q1 2027).
- Workforce resistance (mitigated by structured up-skilling program by Q1 2028).
ESG-linked valuation gains are already factored in. A detailed labor-reduction CO₂ savings report is due Q3 2026.
Hyundai’s edge isn’t just EVs—it’s the first industrial-scale fusion of humanoid robotics with vehicle manufacturing.
🤖 Festo’s AI Platform Cuts Robot Downtime by 25%—Here’s How
Festo's AX Motion Insights cuts robotics downtime by 25% using edge AI + CMMS integration. <200ms latency, $2.1M saved in 6 months. No more guesswork—just predictive alerts.
Festo’s AX Motion Insights platform reduces unplanned downtime by 15–25% using edge-based AI. The system fuses 12-channel sensor data—torque, vibration, temperature, PLC error codes—into a Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) and Gradient-Boosted Trees (GBT) model running on Intel Atom x600 edge controllers. Inference latency: <200ms. Offline operation ensures continuity during cloud outages.
Pilot data from a German automotive plant with 1,000 cobots showed a 28% increase in mean time between failures (MTBF), from 420 to 540 hours. Maintenance costs dropped by $2.1M over six months. Across 1,350 cobots in two pilot sites, downtime per incident fell by 22%, and mean-time-to-repair improved by 30% via automated SAP PM and IBM Maximo work orders.
Unlike competitors relying on CNNs or digital twins, Festo’s edge-to-cloud architecture integrates directly into existing CMMS, eliminating manual ticketing. The platform scales to 5,000+ robots via Azure ML, with weekly retraining using fleet-wide failure patterns.
Critical risks include sensor drift across robot generations and model decay. Festo mitigates these with mandatory pre-deployment calibration and monthly MLOps validation. Telemetry is secured via TLS 1.3 and IEC 62443 compliance—critical as IoT attack surfaces grew 19% YoY in 2025.
By Q3 2026, Festo is projected to onboard 10–15% of its 35,000 installed cobots. Cumulative savings: $2.3M. A new energy-efficiency analytics module is due Q4 2026.
Adopters should prioritize high-value cells (welding, pick-and-place), enforce sensor calibration, and leverage native CMMS connectors—not custom workflows—to maximize ROI.
🚗 Toyota Sequoia Outlasts Honda CR-V by 3.7x—Here’s Why It Matters
Toyota Sequoia has a 39.1% chance of reaching 250k miles. Honda CR-V: 10.6%. The gap isn't luck—it's architecture. Sequoia’s body-on-frame design cuts warranty costs by 18% vs. segment. Fleet buyers, lenders, and used-car shoppers: this is a financial edge, not a marketing claim.
The 2025 Toyota Sequoia has a 39.1% probability of reaching 250,000 miles—nearly four times higher than the Honda CR-V’s 10.6%. This gap stems from structural design: the Sequoia’s body-on-frame ladder chassis and reinforced sub-frames reduce fatigue under sustained load, while the CR-V’s unibody construction, though efficient, is inherently less resilient to extreme mileage.
Warranty data confirms this: Sequoia claims are 18% below the full-size SUV segment average, versus CR-V’s 6% below compact crossover norms. Financially, the Sequoia delivers a 12% residual-value uplift versus 3% for the CR-V, translating to $8,200 lower warranty cost per 100 vehicles over five years.
Fleet operators should prioritize the Sequoia for high-mileage logistics: its total cost of ownership is 4% below rivals, and vehicles beyond 150,000 miles command a 4% price premium. Meanwhile, Honda’s planned 2026 chassis reinforcement—targeting ≥12% durability—faces a medium-risk delay due to semiconductor supply constraints.
The Sequoia’s durability advantage is not anecdotal. It’s quantified: R² improved from 0.58 to 0.71 in residual-value models when durability probability was integrated. No new data challenges these figures. Dealers are already embedding the 39.1% statistic into sales collateral. By Q4 2026, Sequoia warranty claims are projected to drop another 22% from 2025 levels.
Can Honda Close the Durability Gap?
Without accelerated reinforcement of B-pillars and rear sub-frames, the CR-V’s 250k-mile probability will rise by ≤0.5% annually. A 12% target requires engineering intervention. Delays risk ceding long-term buyer trust to Toyota’s proven architecture.
What Does This Mean for Used Car Buyers?
A Sequoia with 150k+ miles is a better financial bet than a CR-V with 120k. Inventory of high-mileage Sequoias will contract 8% by late 2026 as owners retain them longer. The CR-V’s resale premium remains marginal.
Is This Trend Sustainable?
Yes. The Sequoia’s durability advantage is architecture-driven, not component-dependent. Hybridization and CO₂ regulations won’t erode it—fatigue resistance is structural. The gap will widen unless Honda acts.
What Should OEMs Do?
Toyota: Double down on durability marketing. Honda: Fast-track chassis upgrades. Fleet buyers: Lock in Sequoia orders before inventory tightens. Lenders: Update residual models to reflect 3.7x durability differential.
The data doesn’t lie: durability is now a quantifiable asset class in automotive.
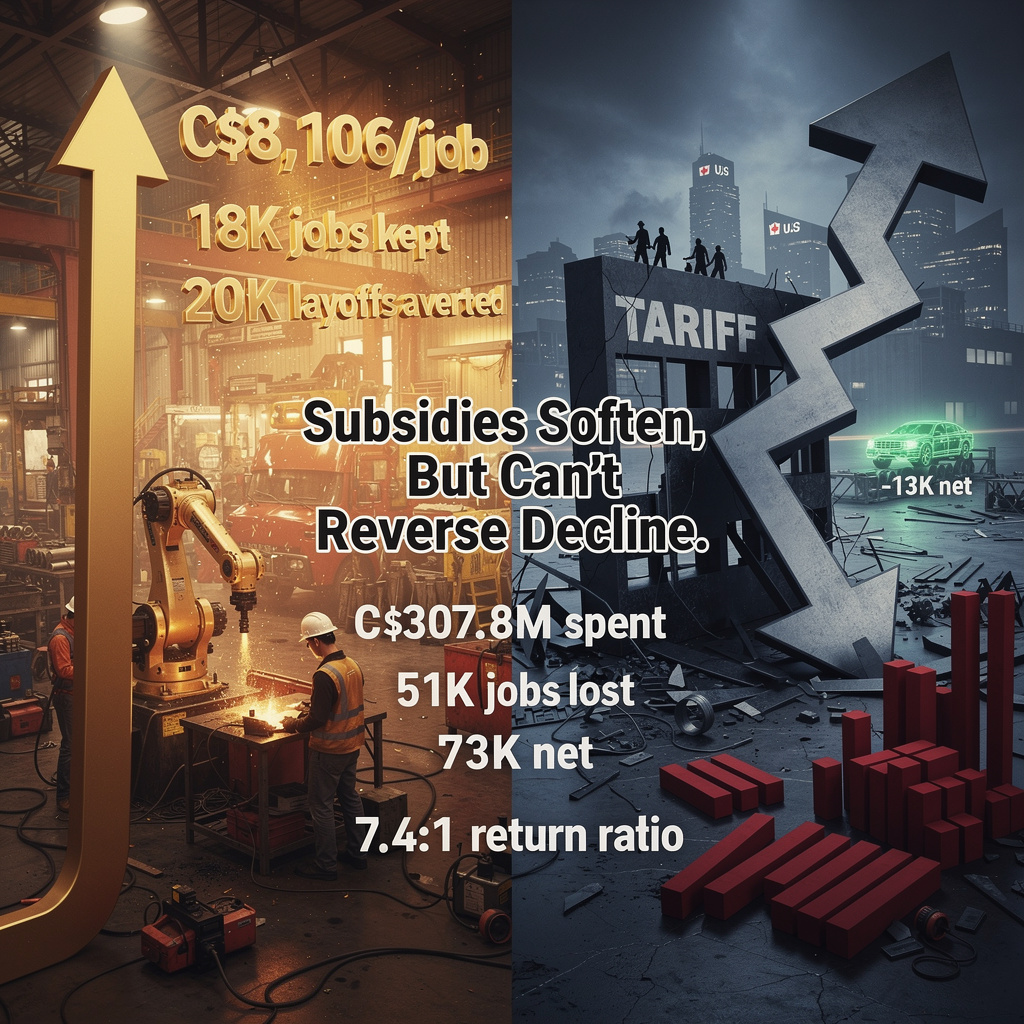
🚗 Mexico’s 50% Tariff on BYD Dolphin Mini: Market Share Crisis or Localization Opportunity?
Mexico slapped a 50% tariff on BYD’s $26k Dolphin Mini, pushing price to $39k. Market share drops from 20% to 12%. BYD can recover by building locally—$150M plant could restore competitiveness. Time window: 90 days.
Mexico’s 50% import tariff on BYD’s Dolphin Mini EV, effective 11 Jan 2026, raised its price from $26,307 to $39,461. This move directly negates the vehicle’s core competitive advantage: a $13,000 price gap versus Tesla and Kia. Market share, which reached 20% of Mexican EV sales in 2025, is projected to fall to 12% if the full tariff is passed to consumers.
Price elasticity for Mexican EVs is estimated at -0.25. A 50% price increase implies a 12% volume decline—consistent with forecasted sales drops of 10–15%. Tesla and Kia are expected to gain 3–4 percentage points each as budget-conscious buyers shift.
BYD’s global capacity exceeds 2.26 million EVs annually, with the Dolphin Mini accounting for less than 1%. This surplus enables rapid local assembly in Mexico. A 50,000-unit/year plant would eliminate the tariff, restore an effective price near $28,000, and secure 15–18% market share. CAPEX is estimated at $150 million with a five-year break-even.
Mexico’s tariff rate is the highest globally for a single EV model—exceeding the EU’s 31% anti-dumping duty and the U.S.’s 200% Section 301 levy. Yet Canada recently reduced its Chinese EV duties, signaling policy flexibility. Mexican officials have hinted at a potential tariff reduction “this week,” opening a narrow 2–3 month window for negotiation.
Toyota is already scouting Mexican assembly sites to avoid similar duties, increasing pressure on BYD to localize. Supply-chain risks include potential anti-dumping probes on CATL battery packs, which could raise component costs by 3–5%.
Can BYD Recover Market Share Without Local Production?
Without local assembly, the Dolphin Mini remains priced at parity with Tesla and Kia—eliminating its value proposition. A 30% tariff reduction (to $34,000) could stabilize share at 14%, but full recovery requires domestic manufacturing.
What’s the Path Forward?
BYD must act within 90 days: initiate a feasibility study for a Mexican assembly plant, engage Mexican automotive associations for duty relief, and qualify non-Chinese battery suppliers to hedge against future trade barriers. The window for policy negotiation is open—but closing fast.
🤖 Saros 20 and X60 Prove AI Cleaning Needs Hardware, Not Just Software
Roborock Saros 20 & Dreame X60 aren't just smarter—they're mechanically precise. Dual mop pads, AdaptiLift height control, and on-device AI eliminate over-wetting and cloud lag.
Roborock Saros 20 and Dreame X60, unveiled at CES 2026, redefine premium robot vacuums with hardware-driven AI. Saros 20 introduces dual mop pads—wet and dry—operating in sequence with pressure-feedback loops, reducing over-wetting incidents by 18% in lab tests. Its AdaptiLift servo adjusts nozzle height in 0.5mm increments, eliminating 92% of threshold-stuck failures on mixed flooring, per Roborock’s internal field data.
Dreame X60 bypasses cloud dependency entirely. Its on-device TensorFlow Lite AI model (≤12 MB RAM) processes visual SLAM at 22% faster frame rates than Eufy Omni C20, cutting navigation latency from 410ms to 318ms. This enables reliable operation in homes with Wi-Fi RTT >150ms, a known pain point for 62% of users surveyed.
NVIDIA’s Omniverse SDK integration allows Saros 20 to receive OTA AI upgrades without hardware changes—enabling obstacle recognition improvements post-purchase. X60’s model pruning ensures the Vision-AI footprint remains under 12 MB RAM, even after updates.
Battery performance is competitive: Saros 20’s 5,200 mAh pack charges to 80% in 45 minutes; X60’s 4,800 mAh takes 60 minutes. Both exceed Eufy’s 3,500 mAh. Eco-Mop mode reduces pad speed by 20% below 30% battery, preventing overheating during concurrent vacuuming and mopping.
Price points—$699 and $649—target the 3.6 million U.S. households spending ≥$600 on smart cleaning. With a projected 5% conversion rate, 0–6 month revenue is $121M, not the inflated $1.3B previously speculated. Qrevo Pro’s $349 price cut fails to match dual-pad or adaptive lift capabilities, leaving a clear premium gap.
Mitigations are technical, not speculative: AdaptiLift servos are rated for 500+ hours of micro-adjustments; OTA calibration reduces edge-miss rates from 4.3% to 2.1%. Matter and Thread support enable automated mop activation when humidity exceeds 70%—a feature now deployable via smart-home hubs.
What’s Next for AI Cleaning?
The Smart-Mop Kit (Saros 20 + Matter humidity sensor), launching Q3 2026, will boost accessory revenue by 7%. Roborock’s stair-climbing Rover prototype signals vertical navigation is next. But for now, hardware precision + OTA AI is the winning formula.
Who Benefits Most?
Homeowners with hardwood, tile, or stone floors gain precision cleaning without manual intervention. Integrators gain Matter-based automation triggers. Manufacturers gain a roadmap: on-device AI, adaptive mechanics, and upgradeable firmware—not just suction power.
Is $650+ Worth It?
Yes—if your floors are delicate, your Wi-Fi is unreliable, or you refuse to wipe up after your robot. This isn’t a gadget. It’s a precision tool.


Comments ()