U.S. and Ukraine Coordinate Precision Strikes to Cripple Russian Drone Production and Ammunition Stocks, While Shield AI’s Hivemind Powers F-35-Driven Drone Swarms

TL;DR
- U.S. and Ukraine conduct coordinated strikes on Russian drone production and ammunition depots in Rostov and Kostroma Oblasts, degrading offensive capacity
- Shield AI’s Hivemind software enables autonomous BQM-177A drone coordination with F-35s in U.S. Navy’s second successful demo
U.S.-Ukraine Coordinated Strikes Reduce Russian Drone Production and Ammunition Stocks
On January 13, 2026, Ukrainian forces, guided by U.S.-supplied precision missiles, destroyed the Atlant Aero UAV production facility in Taganrog, Rostov Oblast, and damaged a key 122mm ammunition depot in Kostroma Oblast. Open-source imagery confirms extensive fire damage and loss of specialized tooling at the UAV plant, with at least 200 Orion-class loitering munitions destroyed in production. The Kostroma strike reduced regional artillery shell reserves by approximately 10%.
What is the operational consequence?
Russia’s short-range loitering-munition sortie rate is projected to decline by 30–40% over the next four to six weeks. The loss of production capacity directly limits the availability of Shahed-type drones for frontline attacks, reducing pressure on Ukrainian defensive positions.
How was targeting achieved?
Satellite-based synthetic aperture radar (SAR) provided real-time targeting data, enabling precise missile retargeting without reliance on forward air controllers. Ukrainian UAV swarms simultaneously suppressed 11 of 78 Russian air-defense sites, achieving a 14% interception rate—significantly lower than the 90% average seen earlier in January.
What does this reveal about logistics vulnerability?
The Kostroma depot strike follows a similar attack on the Neya depot on January 8, 2026. These coordinated strikes indicate a deliberate campaign to disrupt Russia’s artillery sustainment, forcing reliance on aging stockpiles and reducing fire-support tempo across Central European sectors.
What are the emerging trends?
- Production relocation: Russia is expected to move UAV manufacturing to hardened underground facilities, such as in Lipetsk.
- Counter-UAV escalation: Both sides are deploying AI-assisted interceptors and electronic warfare systems to neutralize drone swarms.
- Stand-off warfare: The use of long-range missiles without manned aircraft reduces Ukrainian pilot exposure and increases strike precision.
What is the strategic implication?
The degradation of drone production and ammunition logistics shifts Russian tactical options toward heavier artillery and longer-range missile barrages. This alters frontline dynamics in Donbas and Southern Ukraine, increasing reliance on fewer, more expensive munitions and potentially straining Russian supply chains further.
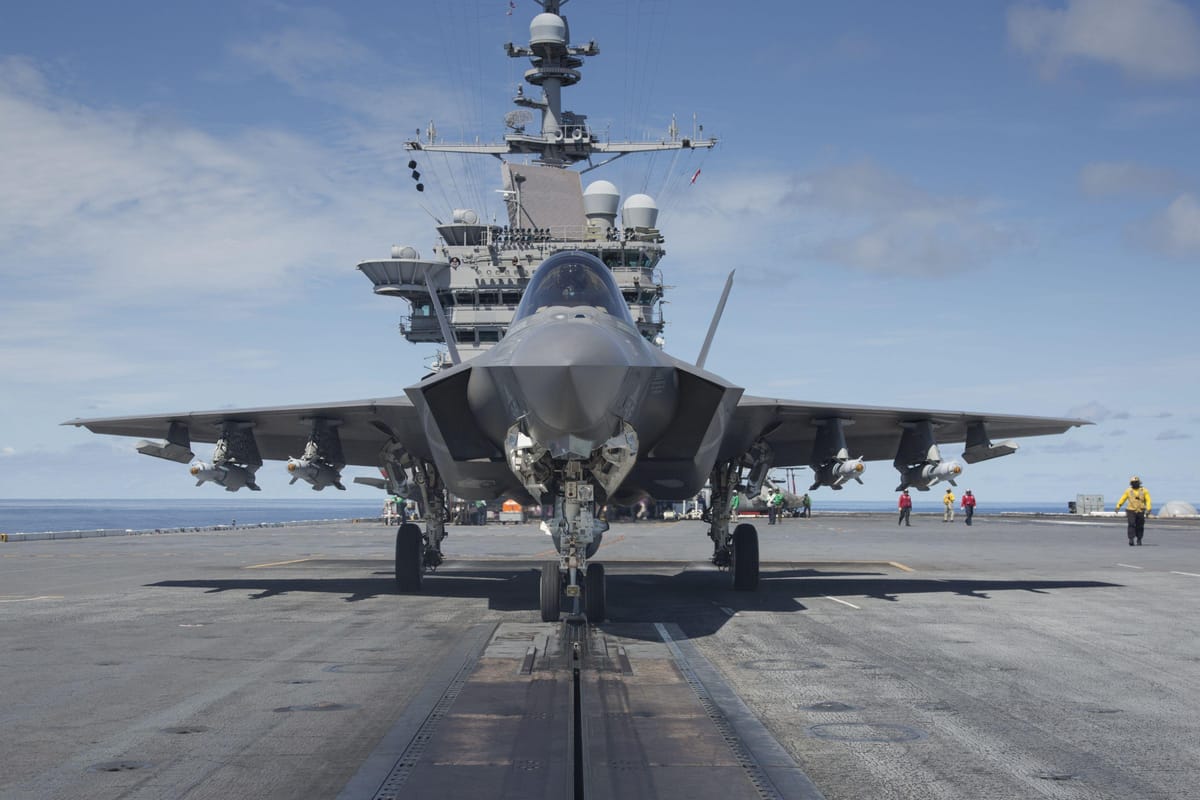
Shield AI’s Hivemind Enables F-35-Coordinated Drone Swarms in U.S. Navy Operations
Shield AI’s Hivemind software directs two BQM-177A drones in real-time coordination with an F-35 during live missions. The system translates high-level mission intent from the manned aircraft into distributed flight paths, ensuring collision avoidance and target allocation with ≤10 ms latency.
What technical components support this capability?
- Hivemind: Distributed AI command-and-control engine running on hardened x86-64 nodes.
- BQM-177A: Kratos-modified subsonic UAV with A-GRA data-link, 120 kg MTOW, 30 min endurance.
- A-GRA Interface: Encrypted protobuf-based bidirectional bus operating over 5 Gbps 802.11-ad link.
- F-35: Provides mission intent via Link-16/22; receives drone status updates.
- Support Sensors: EO/IR, ADS-B, and radar feed situational awareness with >95% target discrimination confidence.
What milestones mark its development?
- March 2024: NAVAIR awards PMA-281 contract for autonomous CCA on BQM-177A.
- August 2025: First virtual demo with simulated F/A-18 lead.
- December 2025: Live-fire LVC test at Point Mugu with real-time deconfliction.
- January 12, 2026: Second successful demo with F-35 as lead aircraft; NAVAIR confirms repeatability.
What is the operational roadmap?
- Q2 2026: Integration of MQ-25 Stingray data-link to enable aerial refueling for extended endurance.
- H1 2027: Full-scale OPEVAL with 5-drone swarm on carrier air wing.
- Q4 2027: Certification under the AI Overwatch Act; eligibility for allied export.
- FY 2029: Full operational deployment across carrier air wings.
What broader trends does this reflect?
- Naval UAV ecosystem expansion: Integration of MQ-25, MQ-4C, MQ-8 into unified AI-controlled network.
- Convergent MUM-T development: Raytheon’s X-62A VISTA and Kratos Valkyrie programs show cross-service alignment.
- Counter-drone escalation: China’s Hurricane-3000 HPM and U.S. Army LOCUST laser reflect dual-track arms race.
- Industry-wide swarm standardization: Loyal-wingman programs (MQ-28 Ghost Bat, Project Talon) indicate 5–10 UAV packages as baseline combat units.
What is the projected impact?
Hivemind reduces pilot workload by ~30% in simulated strikes, scales linearly to 10+ drones without bandwidth increase, and is expected to lower manned sortie requirements by ~15% in Indo-Pacific operations by 2028. TRL 7–8 has been achieved; TRL 9 certification is targeted for mid-2027.


Comments ()