Court Overturns GOP Maps, Navy Expands Caribbean Operations, Shutdown Yields $16B Salary Chaos

TL;DR
- US Senators Push Filibuster to Preserve Legislative Leverage
- Redistricting Controversy Persists as Courts Overturn GOP Maps
- US Naval Deployment to Caribbean Escalates Spike in Drug‑Interdiction Strikes
- CSIS Bolsters Arctic Intelligence amid Russia and China Interest
- Government Shutdown Cost $16B in Unpaid Federal Salaries and Fell on Public Services
Judicial Pushback Curbs GOP Redistricting Push Ahead of 2026 Midterms
State Court Interventions
- Utah District Court Judge Dianna Gibson found the newly drawn congressional map unconstitutional under the state's Proposition 4 reforms, forcing GOP leaders to submit an alternative plan.
- Virginia’s Supreme Court applied a 1912 precedent to deny standing to county clerks, allowing the legislature’s map to proceed despite Democratic objections.
- A constitutional challenge in Missouri, filed by the NAACP and state officials, questions whether the current constitution permits mid‑decade redistricting; a trial is set for Nov 25.
Federal Action in California
- California voters approved Proposition 50 (5.6 million yes, 3.2 million no), directing the creation of districts that increase Latino‑voter influence.
- The Department of Justice filed two separate suits alleging that the Proposition 50 map uses race as a proxy for partisan advantage, seeking a preliminary injunction before the 2026 elections.
Voter‑Driven Reform Trends
- Direct‑democracy measures such as Proposition 50 and similar initiatives in Colorado demonstrate growing public involvement in map design.
- Targeted demographic adjustments, notably the emphasis on Latino populations in California, align with recent voting patterns where 68 % of Latino voters supported Democratic candidates in benchmark districts.
Projected Impact on the 2026 House Composition
- Current House balance stands at 219 Republicans to 214 Democrats.
- If Utah and Missouri challenges succeed, the Republican goal of adding 5‑7 seats through mid‑decade redistricting could be reduced by 2‑3 seats.
- Implementation of Proposition 50, pending DOJ resolution, could introduce up to five Democratic‑leaning seats from California, potentially shifting the majority.
- Combined legal outcomes suggest a narrower Republican advantage heading into the 2026 midterms, with a realistic scenario of a Democratic plurality if all pending injunctions are granted.
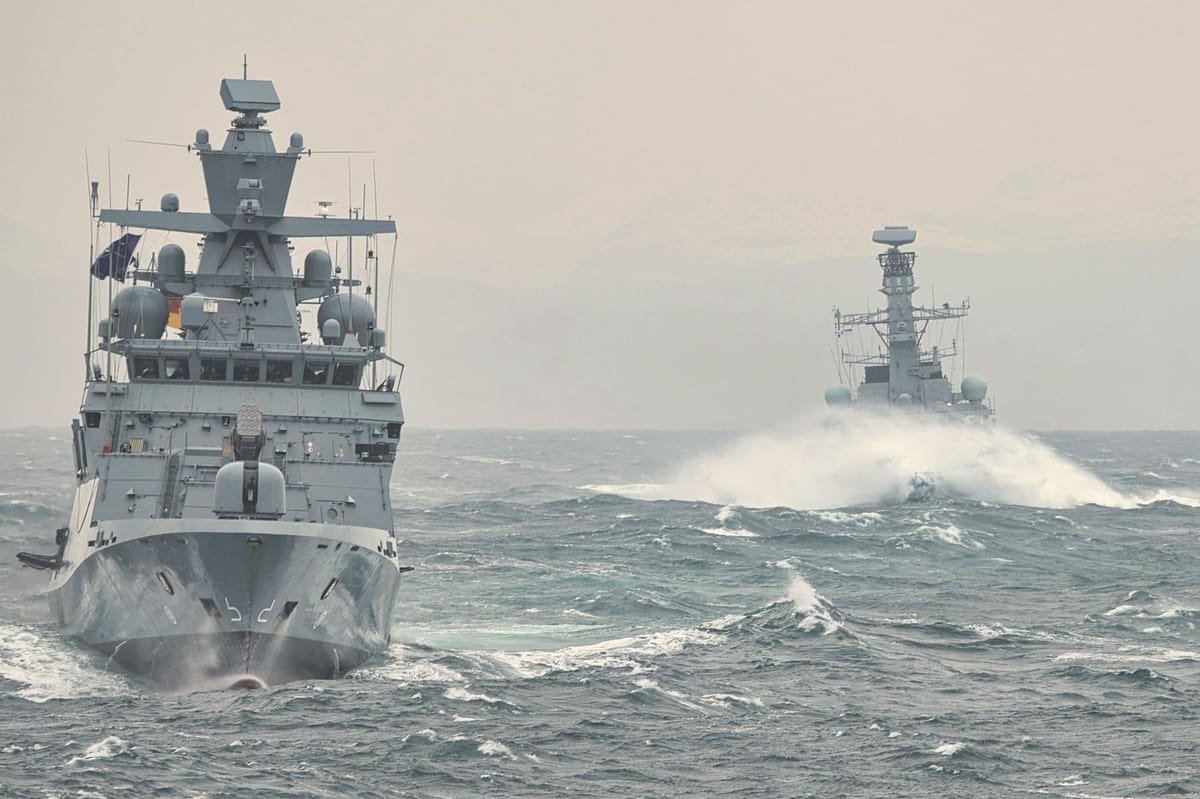
US Naval Surge in the Caribbean: A Calculated Power Play or Legal Quagmire?
Escalating Force
- USS Gerald R. Ford (CVN‑78) deployed with four destroyers, a nuclear‑submarine, and nine air squadrons (≈90 aircraft, including F‑35s and EA‑6).
- Surface combatant count rose to 12‑15 ships; personnel presence reached ~15,000 troops, including 4,500 sailors aboard the carrier.
- Operational cost estimated at $8 M per day for the carrier group.
Kinetic Spike
- 19‑21 strikes recorded from early September to mid‑November 2025.
- Fatalities total 75‑80, with 11 deaths reported on 12‑13 Nov alone.
- Targets identified as vessels allegedly transporting narcotics from Venezuela and other TCOs.
Political Weaponization
- Executive order retitled the Department of Defense as the “Department of War”.
- Hegseth’s directive classified drug traffickers as “narco‑terrorists”, framing kinetic action as regime‑change pressure on Maduro.
- Trump administration briefing outlined potential escalation to land‑based options.
International Backlash
- UK, Colombia, and France suspended intelligence sharing following the surge.
- G7 ministers publicly questioned the legality of the strikes.
- UN Human Rights chief described the actions as “extrajudicial killings”.
Legal Ambiguity
- DOJ memorandum extends liability protection to deployed personnel.
- Scholars debate applicability of Article II war powers versus law‑enforcement authority.
- Classification of drug traffickers as combatants remains contested under international humanitarian law.
Risk Landscape
- Medium‑high likelihood of land‑operation authorization, which could draw Russian involvement and regional destabilization.
- High probability of intensified legal challenges from UN bodies and allied nations.
- Potential degradation of intelligence cooperation, reducing operational precision and increasing collateral risk.
Future Outlook (3‑6 months)
- Projected continuation of ≥5 strikes per month, pushing cumulative deaths above 100 by year‑end.
- Congressional hearings expected to demand a formal war‑powers justification; absence of such may trigger a temporary kinetic pause.
- Diplomatic re‑engagement with the UK and Colombia contingent on a transparent after‑action review.
- Carrier group likely to remain on station through Q1‑2026, with possible addition of amphibious assets if land‑target options receive approval.
43‑Day Federal Shutdown: Quantifiable Costs and Policy Lessons
Payroll Shock and Recovery Timeline
- 1.25 million federal employees furloughed, representing roughly two‑thirds of the civilian workforce.
- Direct wage loss estimated at $16 billion, based on average salaries across agencies.
- Four back‑pay tranches scheduled; first tranche to begin on 19 Nov 2025, with full settlement projected for Feb 2026.
- FAA air‑traffic controllers received 70 % of payments within 24–48 hours, illustrating a successful “super‑check” model that other agencies could adopt.
Public‑Service Disruptions
- National Park Service lost approximately $1 million per day in revenue; full reopening expected within weeks, but six‑month revenue recovery forecast.
- Smithsonian Museums operated with a reduced staff of ~2,600; revenue impact mitigated but not eliminated.
- Education Department laid off 2,117 staff initially, adding 466 later, despite the Federal Employee Fair Treatment Act’s furlough protections.
- IRS walk‑in centers closed, creating a processing backlog that will extend beyond the shutdown’s end.
Transportation and Safety‑Net Impacts
- FAA emergency order cut flights at 40 major airports by 10 % (later adjusted to 6 %).
- State emergency funds in Vermont and Connecticut covered essential air‑traffic controller payroll, preventing broader safety risks.
- LIHEAP funding froze at $4.1 billion; many states delayed heating assistance until 24 Nov 2025.
- SNAP benefits paused; retroactive disbursements to resume once appropriations restart.
Macro‑Economic Assessment
- CBO estimates a $1.2 trillion GDP impact over the six‑week shutdown period.
- Indirect costs—including airline operational losses, park revenue deficits, and delayed federal contracts—range between $7 billion and $14 billion.
Emerging Policy Patterns
- Operational functions resumed quickly after the funding bill, yet payroll systems required staggered processing, creating a temporary cash‑flow mismatch for employees.
- States with pre‑existing emergency reserves demonstrated superior resilience in maintaining critical payrolls and assistance programs.
- Discretionary‑fund‑dependent services (Head Start, National Parks, Smithsonian) showed the greatest revenue volatility.
- Congressional salaries remained protected, highlighting a compensation disparity during shutdown periods.
Short‑Term Outlook
- All back‑pay expected to be completed by Feb 2026, assuming no further shutdown.
- State‑level LIHEAP and SNAP assistance should normalize within three weeks of restored federal funding, though 10–15 % of beneficiaries may experience delayed reimbursements.
- Legislative risk remains high; failure to secure the remaining nine appropriations bills could trigger another shutdown within two months.

Comments ()